Page 22 - MSAM-2-4
P. 22
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Emerging 3D-printed zeolitic gas adsorbents
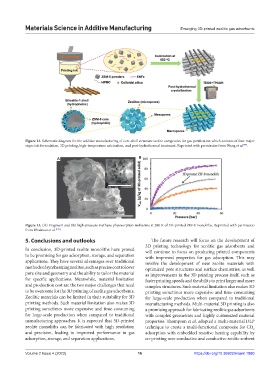
Figure 12. Schematic diagram for the additive manufacturing of core-shell structure zeolite composites for gas purification which consists of four major
steps: ink formulation, 3D printing, high-temperature calcination, and post-hydrothermal treatment. Reprinted with permission from Wang et al. .
[97]
A B
Figure 13. (A) Fragment and (B) high-pressure methane physisorption isotherms at 298 K of 3D-printed ZIF-8 monoliths. Reprinted with permission
from Dhainaut et al. [129] .
5. Conclusions and outlooks The future research will focus on the development of
3D printing technology for zeolitic gas adsorbents and
In conclusion, 3D-printed zeolite monoliths have proved will continue to focus on producing printed components
to be promising for gas adsorption, storage, and separation with improved properties for gas adsorption. This may
applications. They have several advantages over traditional involve the development of new zeolite materials with
methods of synthesizing zeolites, such as precise control over optimized pore structures and surface chemistries, as well
pore size and geometry and the ability to tailor the material as improvements in the 3D printing process itself, such as
for specific applications. Meanwhile, material limitation faster printing speeds and the ability to print larger and more
and production cost are the two major challenges that need complex structures. Such material limitation also makes 3D
to be overcome for the 3D printing of zeolite gas adsorbents. printing sometimes more expensive and time-consuming
Zeolitic materials can be limited in their suitability for 3D for large-scale production when compared to traditional
printing methods. Such material limitation also makes 3D manufacturing methods. Multi-material 3D printing is also
printing sometimes more expensive and time-consuming a promising approach for fabricating zeolitic gas adsorbents
for large-scale production when compared to traditional with complex geometries and highly customized material
manufacturing approaches. It is expected that 3D-printed properties. Thompson et al. adopted a multi-material DLP
zeolite monoliths can be fabricated with high resolution technique to create a multi-functional composite for CO
2
and precision, leading to improved performance in gas adsorption with embedded resistive heating capability by
adsorption, storage, and separation applications. co-printing non-conductive and conductive zeolite sorbent
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 16 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.1880