Page 39 - MSAM-4-1
P. 39
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing TPMS for perfect sound absorption
A B
C D
E
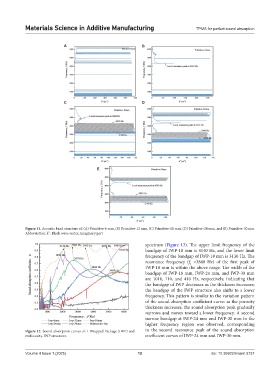
Figure 11. Acoustic band structure of: (A) Primitive-6 mm, (B) Primitive-12 mm, (C) Primitive-18 mm, (D) Primitive-24 mm, and (E) Primitive-30 mm
Abbreviation: k”: Bloch wave vector, imaginary part
spectrum (Figure 13). The upper limit frequency of the
bandgap of IWP-18 mm is 4140 Hz, and the lower limit
frequency of the bandgap of IWP-18 mm is 3130 Hz. The
resonance frequency (f =3860 Hz) of the first peak of
1
IWP-18 mm is within the above range. The width of the
bandgap of IWP-18 mm, IWP-24 mm, and IWP-30 mm
are 1010, 710, and 410 Hz, respectively, indicating that
the bandgap of IWP decreases as the thickness increases;
the bandgap of the IWP structure also shifts to a lower
frequency. This pattern is similar to the variation pattern
of the sound absorption coefficient curve: as the porosity
thickness increases, the sound absorption peak gradually
narrows and moves toward a lower frequency. A second
narrow bandgap at IWP-24 mm and IWP-30 mm in the
higher frequency region was observed, corresponding
Figure 12. Sound absorption curves of: I-Wrapped Package (IWP) and to the second resonance peak of the sound absorption
multicavity-IWP structures coefficient curves of IWP-24 mm and IWP-30 mm.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 12 doi: 10.36922/msam.5737