Page 40 - MSAM-4-1
P. 40
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing TPMS for perfect sound absorption
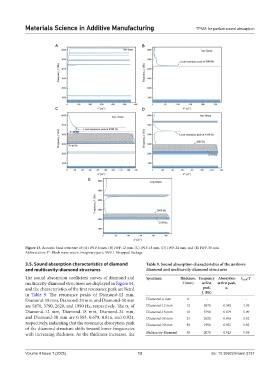
A B
C D
E
Figure 13. Acoustic band structure of: (A) IWP-6 mm, (B) IWP-12 mm, (C) IWP-18 mm, (D) IWP-24 mm, and (E) IWP-30 mm
Abbreviation: k”: Bloch wave vector, imaginary part; IWP: I-Wrapped Package
3.5. Sound absorption characteristics of diamond Table 9. Sound absorption characteristics of the uniform
and multicavity-diamond structures diamond and multicavity‑diamond structures
The sound absorption coefficient curves of diamond and Specimen Thickness, Frequency Absorption λ peak /T
multicavity-diamond structures are displayed in Figure 14, T (mm) at first at first peak,
and the characteristics of the first resonance peak are listed peak, α 1
in Table 9. The resonance peaks of Diamond-12 mm, f 1 (Hz)
Diamond-18 mm, Diamond-24 mm, and Diamond-30 mm Diamond-6 mm 6 - - -
are 5870, 3790, 2620, and 1990 Hz, respectively. The α of Diamond-12 mm 12 5870 0.583 4.93
1
Diamond-12 mm, Diamond-18 mm, Diamond-24 mm, Diamond-18 mm 18 3790 0.679 5.09
and Diamond-30 mm are 0.583, 0.679, 0.816, and 0.921, Diamond-24 mm 24 2620 0.816 5.52
respectively, indicating that the resonance absorption peak Diamond-30 mm 30 1990 0.921 5.82
of the diamond structure shifts toward lower frequencies
with increasing thickness. As the thickness increases, the Multicavity-Diamond 30 2070 0.923 5.59
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 13 doi: 10.36922/msam.5737