Page 129 - OR-1-2
P. 129
A B C
D E
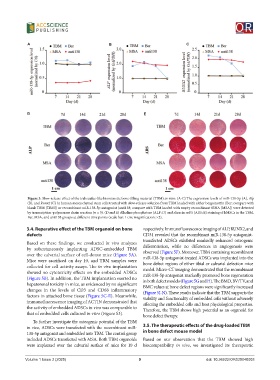
Figure 3. Slow-release effect of the trabeculae-like biomimetic bone-filling material (TBM) in vitro. (A-C) The expression levels of miR-138-5p (A), Alp
(B), and Runx2 (C) in human mesenchymal stem cells treated with slow-release solution from TBM loaded with either bergamottin (Ber; compare with
blank TBM [TBM]) or recombinant miR-138-5p antagonist (anti138; compare with TBM loaded with empty recombinant tRNA [MSA]) were detected
by transcription-polymerase chain reaction (n = 3). (D and E) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP; D) and alizarin red S (ARS; E) staining of hMSCs in the TBM,
Ber, MSA, and anti138 groups at different time points (scale bar: 1 cm; magnification: ×2).
3.4. Reparative effect of the TBM organoid on bone respectively. Immunofluorescence imaging of ALP, RUNX2, and
defects CD31 revealed that the recombinant miR-138-5p antagonist-
transfected ADSCs exhibited markedly enhanced osteogenic
Based on these findings, we conducted in vivo analyzes
by subcutaneously implanting ADSC-embedded TBM differentiation, while no differences in angiogenesis were
over the calvarial surface of cell-donor mice (Figure 5A). observed (Figure 5F). Moreover, TBM containing recombinant
miR-138-5p antagonist-treated ADSCs was implanted into the
Mice were sacrificed on day 10, and TBM samples were
collected for cell activity assays. The in vivo implantation bone defect regions of either tibial or calvarial defection mice
model. Micro-CT imaging demonstrated that the recombinant
showed no cytotoxicity effects on the embedded ADSCs miR-138-5p antagonist markedly promoted bone regeneration
(Figure 5B). In addition, the TBM implantation exerted no in both defect models (Figure 5G and H). The BMD, BV/TV, and
hepatorenal toxicity in mice, as evidenced by no significant BMC values at bone defect regions were significantly increased
changes in the levels of CD3 and CD68 inflammatory (Figure 5I-N). These results indicate that the TBM supports the
factors in attached bone tissue (Figure 5C-E). Meanwhile, viability and functionality of embedded cells without adversely
immunofluorescence imaging of ACTIN demonstrated that affecting the embedded cells and host physiological properties.
the activity of embedded ADSCs in vivo was comparable to Therefore, the TBM shows high potential as an organoid for
that of embedded cells cultured in vitro (Figure S3).
bone defect therapy.
To further investigate the osteogenic potential of the TBM
in vivo, ADSCs were transfected with the recombinant miR- 3.5. The therapeutic effects of the drug-loaded TBM
138-5p antagonist and embedded into TBM. The control group in bone defect mouse model
included ADSCs transfected with MSA. Both TBM organoids Based on our observation that the TBM showed high
were implanted over the calvarial surface of mice for 10 d biocompatibility in vivo, we investigated its therapeutic
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/OR025040003