Page 126 - OR-1-2
P. 126
A B
C
D E F
G H I
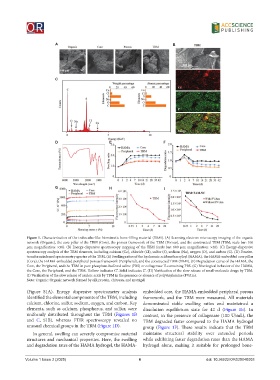
Figure 1. Characterization of the trabeculae-like biomimetic bone-filling material (TBM). (A) Scanning electron microscopy imaging of the organic
network (Organic), the core pillar of the TBM (Core), the porous framework of the TBM (Porous), and the constructed TBM (TBM; scale bar: 100
μm; magnification: ×50). (B) Energy-dispersive spectroscopy mapping of the TBM (scale bar: 600 μm; magnification: ×40). (C) Energy-dispersive
spectroscopy analysis of the TBM elements, including calcium (Ca), chloride (Cl), sulfur (S), sodium (Na), oxygen (O), and carbon (C). (D) Fourier-
transform infrared spectrometry spectra of the TBM. (E) Swelling ratios of the hyaluronic acid methacryloyl (HAMA), the HAMA-embedded core pillar
(Core), the HAMA-embedded peripheral porous framework (Peripheral), and the constructed TBM (TBM). (F) Degradation curve of the HAMA, the
Core, the Peripheral, and the TBM in pure phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or collagenase II-containing PBS. (G) Rheological behavior of the HAMA,
the Core, the Peripheral, and the TBM. Hollow indicates G”. Solid indicates G’. (H) Verification of the slow release of small-molecule drugs by TBM.
(I) Verification of the slow release of nucleic acids by TBM in the presence or absence of polyvinylamine (PVAm).
Note: Organic: Organic network formed by silk protein, chitosan, and matrigel.
(Figure S1A). Energy dispersive spectrometry analysis embedded core, the HAMA-embedded peripheral porous
identified the elemental components of the TBM, including framework, and the TBM were measured. All materials
calcium, chlorine, sulfur, sodium, oxygen, and carbon. Key demonstrated stable swelling ratios and maintained a
elements, such as calcium, phosphorus, and sulfur, were dissolution equilibrium state for 42 d (Figure 1E). In
uniformly distributed throughout the TBM (Figures 1B contrast, in the presence of collagenase (100 U/mL), the
and C, S1B), whereas FTIR spectroscopy revealed no TBM degraded faster compared to the HAMA hydrogel
unusual chemical groups in the TBM (Figure 1D). group (Figure 1F). These results indicate that the TBM
In general, swelling can severely compromise material maintains structural stability over extended periods
structures and mechanical properties. Here, the swelling while exhibiting faster degradation rates than the HAMA
and degradation rates of the HAMA hydrogel, the HAMA- hydrogel alone, making it suitable for prolonged bone-
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/OR025040003