Page 137 - OR-1-2
P. 137
A B
C
D
E F G
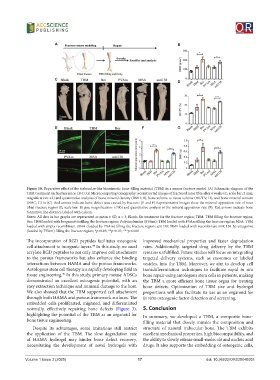
Figure 10. Reparative effect of the trabeculae-like biomimetic bone-filling material (TBM) in a mouse fracture model. (A) Schematic diagram of the
TBM treatment on fracture mice. (B-D, G) Microcomputing tomography reconstructed images of fractured mice tibia after 4 weeks (C; scale bar: 2 mm;
magnification: ×2) and quantitative analyzes of bone mineral density (BMD; B), bone volume to tissue volume (BV/TV; D), and bone mineral content
(BMC; G) in (C). Red arrows indicate bone defect area caused by fracture. (E and F) Representative images show the mineral apposition rate of mice
tibial fracture region (E; scale bar: 10 μm; magnification: ×700) and quantitative analysis of the mineral apposition rate (F). Red arrows indicate bone
formation line distance labeled with calcein.
Notes: All data in bar graphs are represented as mean ± SD, n = 3; Blank: No treatment for the fracture region; TBM: TBM filling the fracture region;
Ber: TBM loaded with bergamottin filling the fracture region; Polyvinylamine (PVAm): TBM loaded with PVAm filling the fracture region; MSA: TBM
loaded with empty recombinant tRNA (loaded by PVAm) filling the fracture region; anti138: TBM loaded with recombinant miR-138-5p antagonist
(loaded by PVAm) filling the fracture region; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
The incorporation of RGD peptides facilitates osteogenic improved mechanical properties and faster degradation
cell attachment to inorganic layers. In this study, we used rates. Additionally, targeted drug delivery by the TBM
44
acrylate RGD peptides to not only improve cell attachment remains unfulfilled. Future studies will focus on integrating
to the porous frameworks but also enhance the binding targeted delivery systems, such as exosomes or labeled
interactions between HAMA and the porous frameworks. vesicles, into the TBM. Moreover, we aim to develop cell
Autologous stem cell therapy is a rapidly developing field in transdifferentiation techniques to facilitate rapid in situ
tissue engineering. In this study, primary mouse ADSCs bone repair using autologous stem cells in patients, making
45
demonstrated an excellent osteogenic potential, with an the TBM a more efficient bone tissue organ for treating
easy extraction technique and minimal damage to the host. bone defects. Optimization of TBM size and hydrogel
We also showed that the TBM supported cell attachment proportions will also facilitate its use as an organoid for
through both HAMA and porous framework surfaces. The in vitro osteogenic factor detection and screening.
embedded cells proliferated, migrated, and differentiated
normally, effectively repairing bone defects (Figure 3), 5. Conclusion
highlighting the potential of the TBM as an organoid for In summary, we developed a TBM, a composite bone-
bone tissue engineering. filling material that closely mimics the composition and
Despite its advantages, some imitations still restrict structure of natural trabecular bone. The TBM exhibits
the application of the TBM. The slow degradation rate excellent mechanical properties, high biocompatibility, and
of HAMA hydrogel may hinder bone defect recovery, the ability to slowly release small-molecule and nucleic acid
necessitating the development of novel hydrogels with drugs. It also supports the embedding of osteogenic cells,
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 17 doi: 10.36922/OR025040003