Page 99 - OR-1-2
P. 99
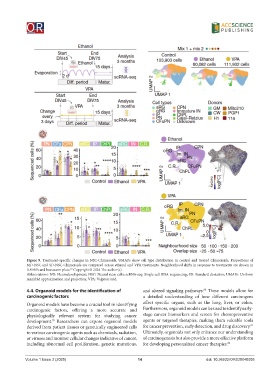
Figure 9. Treatment-specific changes in NSC-Chimeroids. UMAPs show cell type distribution in control and treated Chimeroids. Proportions of
MD-NSC and SD-NSC-Chimeroids are compared across ethanol and VPA treatments. Neighborhood shifts in response to treatments are shown in
UMAPs and beeswarm plots. Copyright © 2024 The author(s).
69
Abbreviations: ND: Neurodevelopment; NSC: Neural stem cells; scRNA-seq: Single-cell RNA sequencing; SD: Standard deviation; UMAPs: Uniform
manifold approximation and projection; VPA: Valproic acid.
4.4. Organoid models for the identification of and altered signaling pathways. These models allow for
80
carcinogenic factors a detailed understanding of how different carcinogens
Organoid models have become a crucial tool in identifying affect specific organs, such as the lung, liver, or colon.
carcinogenic factors, offering a more accurate and Furthermore, organoid models can be used to identify early-
physiologically relevant system for studying cancer stage cancer biomarkers and screen for chemopreventive
development. Researchers can expose organoid models agents or targeted therapies, making them valuable tools
79
81
derived from patient tissues or genetically engineered cells for cancer prevention, early detection, and drug discovery.
to various carcinogenic agents such as chemicals, radiation, Ultimately, organoids not only enhance our understanding
or viruses and monitor cellular changes indicative of cancer, of carcinogenesis but also provide a more effective platform
including abnormal cell proliferation, genetic mutations, for developing personalized cancer therapies. 82
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/OR025040005