Page 101 - OR-1-2
P. 101
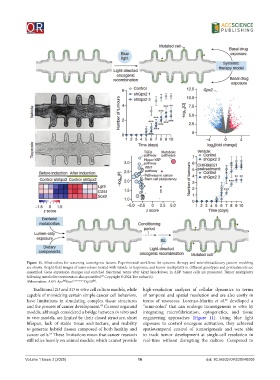
Figure 11. Mini-colons for screening tumorigenic factors. Experimental workflows for systemic therapy and microbiota/dietary pattern modeling
are shown. Bright-field images of mini-colons treated with vehicle or tiopronin, and tumor multiplicity in different genotypes and pretreatments are
quantified. Gene expression changes and enriched functional terms after Gpx2 knockdown in AKP tumor cells are presented. Tumor multiplicity
85
following metabolite treatments is also quantified. Copyright © 2024 The author(s).
fl/fl
fl/fl
Abbreviation: AKP: Apc Kras LSL-G12D/+ Trp53 .
Traditional 2D and 3D in vitro cell culture models, while high-resolution analyses of cellular dynamics in terms
capable of mimicking certain simple cancer cell behaviors, of temporal and spatial resolution and are also costly in
have limitations in simulating complex tissue structures terms of resources. Lorenzo-Martín et al. developed a
85
and the process of cancer development. Current organoid “mini-colon” that can undergo tumorigenesis in vitro by
83
models, although considered a bridge between in vitro and integrating microfabrication, optogenetics, and tissue
in vivo models, are limited by their closed structure, short engineering approaches (Figure 11). Using blue light
lifespan, lack of stable tissue architecture, and inability exposure to control oncogene activation, they achieved
to generate hybrid tissues composed of both healthy and spatiotemporal control of tumorigenesis and were able
84
cancer cells. These limitations mean that cancer research to track tumor development at single-cell resolution in
still relies heavily on animal models, which cannot provide real-time without disrupting the culture. Compared to
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 16 doi: 10.36922/OR025040005