Page 9 - TD-2-1
P. 9
Tumor Discovery RAGEs in oral squamous cell carcinoma
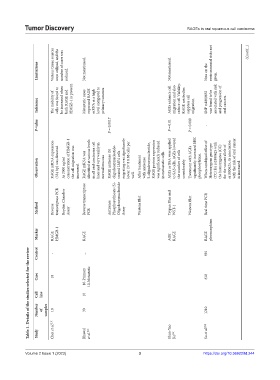
Limitations Various tissue sources were utilized, and the number of cases was reduced. Not mentioned. Not mentioned. Note on the environmental risks not given. (Cont’d...)
Inference The mobility of cells was found to be increased when both RAGE and HMGB-1 is present. Metastatic cases expressed RAGE mRNA at a high level compared to primary tumours AGEs enhance cell migration and also reduce cell Viability. RAGE antibodies suppress cell migration. SNP rs1800652 was found to be associated with risk and progression of oral cancers
P-value P = 0.0017 P = 0.01 P = 0.009 -
Observation RAGE mRNA expression (534 bp) was detected At 2000 ng/ml concentration of HMGB-1 the cell migration was increased. RAGE mRNA was identified at various levels in all oral carcinoma cell lines and very weakly in normal mucosa RAGE antisense (S) oligodeoxynucleotide- treated LMF4 cells migrating was significantly lower (37 8 8.88 cells per well. After treatment with antisense S-oligodeoxynucleotide, RAGE protein
transcriptase PCR Boyden Chamber Reverse transcriptase Phosphorothioate (S)- Oligodeoxynucleotide Trypan Blue and Real time PCR
Method Reverse Assay PCR Antisense Assay Western Blot WST-1 Western Blot
Marker RAGE HMGB-1 RAGE AGE RAGE RAGE pleomorphism
Control - _ 592
Table 1. Details of the studies selected for the review
Case 10 10-Primary 10-Metastatic 618
Cell line 10
Number of samples 10 30 1210
Choi et al. [10] Shun-Yao Su et al. [19]
Study Bhawal et al. [21] Ko [15]
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.244