Page 18 - TD-2-3
P. 18
Tumor Discovery Targeted drug delivery systems for the treatment of tumors
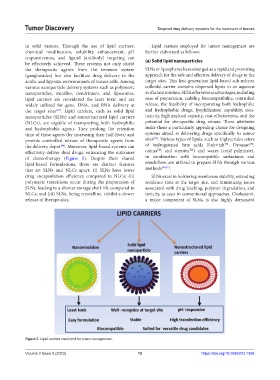
in solid tumors. Through the use of lipid carriers, Lipid carriers employed for tumor management are
chemical modification, solubility enhancement, pH further elaborated as follows:
responsiveness, and ligand (antibody) targeting can
be effectively achieved. These systems not only shield (a) Solid lipid nanoparticles
the therapeutic agents from the immune system SLNs or lipospheres have emerged as a rapid and promising
(gangliosides) but also facilitate drug delivery in the approach for the safe and effective delivery of drugs to the
acidic and hypoxic environments of tumor cells. Among target sites. This first-generation lipid-based sub-micron
various nanoparticle delivery systems such as polymeric colloidal carrier contains dispersed lipids in an aqueous
nanoparticles, micelles, dendrimers, and liposomes, surfactant solution. SLNs offer several advantages, including
lipid carriers are considered the least toxic and are ease of preparation, stability, biocompatibility, controlled
widely utilized for gene, DNA, and RNA delivery at release, the feasibility of incorporating both hydrophilic
the target sites [93] . Lipid carriers, such as solid lipid and hydrophobic drugs, lyophilization capability, non-
nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers toxicity, high payload capacity, cost-effectiveness, and the
(NLCs), are capable of transporting both hydrophilic potential for site-specific drug release. These attributes
and hydrophobic agents. They prolong the retention make them a particularly appealing choice for designing
time of these agents (by increasing their half-lives) and systems aimed at delivering drugs specifically to tumor
[95]
provide controlled release of therapeutic agents from sites . Various types of lipids, such as triglycerides esters
TM
TM
the delivery depot [94] . Moreover, lipid-based systems can of hydrogenated fatty acids (Lubritab , Dynasan ,
TM
TM
effectively deliver dual drugs, enhancing the outcomes cutina , and sterotex ) and waxes (cetyl palmitate),
of chemotherapy (Figure 5). Despite their shared in combination with biocompatible surfactants and
lipid-based formulations, there are distinct features emulsifiers, are utilized to prepare SLNs through various
that set SLNs and NLCs apart: (i) SLNs have lower methods [96,97] .
drug encapsulation efficiency compared to NLCs; (ii) SLNs excel in bolstering membrane stability, extending
polymeric transitions occur during the preparation of residence time at the target site, and minimizing issues
SLNs, leading to a shorter storage shelf-life compared to associated with drug leaching, polymer degradation, and
NLCs; and (iii) SLNs, being crystalline, exhibit a slower toxicity, as seen in conventional approaches. Cholesterol,
release of therapeutics. a major component of SLNs, is also highly demanded
Figure 5. Lipid carriers employed for tumor management.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 12 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.1356