Page 57 - TD-3-1
P. 57
Tumor Discovery Mechanism of Buddleja officinalis against ESCC
A B
C
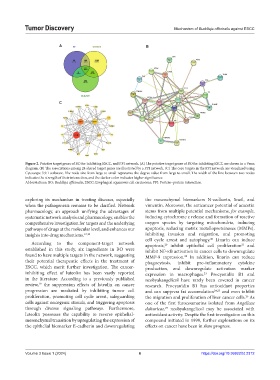
Figure 2. Putative target genes of BO for inhibiting ESCC, and PPI network. (A) The putative target genes of BO for inhibiting ESCC are shown in a Venn
diagram. (B) The associations among 24 shared target genes are illustrated by a PPI network. (C) The core targets in the PPI network are visualized using
Cytoscape 3.9.1 software. The node size from large to small represents the degree value from large to small. The width of the line between two nodes
indicates the strength of their interaction, and the darker color indicates higher significance.
Abbreviations: BO: Buddleja officinalis; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; PPI: Protein–protein interaction.
exploring its mechanism in treating diseases, especially the mesenchymal biomarkers N-cadherin, Snail, and
when the pathogenesis remains to be clarified. Network vimentin. Moreover, the anticancer potential of acacetin
pharmacology, an approach unifying the advantages of stems from multiple potential mechanisms, for example,
systematic network analysis and pharmacology, enables the inducing cytochrome c release and formation of reactive
comprehensive investigation for targets and the underlying oxygen species by targeting mitochondria, inducing
pathways of drugs at the molecular level, and enhances our apoptosis, reducing matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs),
insights into drug mechanisms. 17,18 inhibiting invasion and migration, and promoting
cell cycle arrest and autophagy. Linarin can induce
20
According to the component-target network apoptosis, inhibit epithelial cell proliferation and
21
20
established in this study, six ingredients in BO were inhibit NF-κB activation in cancer cells to downregulate
found to have multiple targets in the network, suggesting MMP-9 expression. In addition, linarin can reduce
22
their potential therapeutic effects in the treatment of phagocytosis, inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine
ESCC, which merit further investigation. The cancer- production, and downregulate activation marker
inhibiting effect of luteolin has been vastly reported expression in macrophages. Procyanidin B1 and
23
in the literature. According to a previously published neobyakangelicol have rarely been covered in cancer
review, the suppression effects of luteolin on cancer research. Procyanidin B1 has antioxidant properties
19
progression are mediated by inhibiting tumor cell and can suppress fat accumulation 24,25 and even inhibit
proliferation, promoting cell cycle arrest, safeguarding the migration and proliferation of liver cancer cells. As
26
cells against oncogenic stimuli, and triggering apoptosis one of the first furocoumarins isolated from Angelicae
through diverse signaling pathways. Furthermore, dahuricae, neobyakangelicol may be associated with
27
luteolin possesses the capability to reverse epithelial- antioxidant activity. Despite the first investigation on this
mesenchymal transition by upregulating the expression of compound initiated in 1999, further explorations on its
the epithelial biomarker E-cadherin and downregulating effects on cancer have been in slow progress.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.2312