Page 59 - TD-3-1
P. 59
Tumor Discovery Mechanism of Buddleja officinalis against ESCC
A
B
C
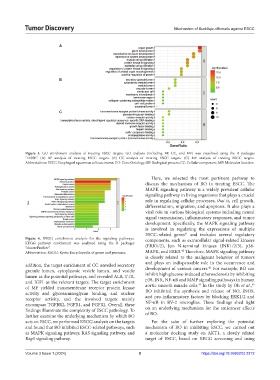
Figure 3. GO enrichment analysis of treating ESCC targets. GO analysis (including BP, CC, and MF) was visualized using the R packages
“DOSE”. (A) BP analysis of treating ESCC targets. (B) CC analysis of treating ESCC targets. (C) MF analysis of treating ESCC targets.
Abbreviations: ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; GO: Gene Ontology; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
Here, we selected the most pertinent pathway to
discuss the mechanism of BO in treating ESCC. The
MAPK signaling pathway is a widely prevalent cellular
signaling pathway in living organisms that plays a crucial
role in regulating cellular processes, that is, cell growth,
differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. It also plays a
vital role in various biological systems including neural
signal transmission, inflammatory responses, and tumor
development. Specifically, the MAPK signaling pathway
is involved in regulating the expressions of multiple
ESCC-related genes and includes several regulatory
41
Figure 4. KEGG enrichment analysis for the signaling pathways. components, such as extracellular signal-related kinases
KEGG pathway enrichment was analyzed using the R packages
“clusterProfiler”. (ERK1/2), Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK1/2/3), p38-
42
Abbreviation: KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes. MAPK, and ERK5. Therefore, MAPK signaling pathway
is closely related to the malignant behavior of tumors
addition, the target enrichment of CC unveiled secretory and plays an indispensable role in the occurrence and
43
granule lumen, cytoplasmic vesicle lumen, and vesicle development of various cancers. For example, BO can
lumen as the potential pathways, and revealed ALB, TTR, inhibit high glucose-induced atherosclerosis by inhibiting
and IGF1 as the relevant targets. The target enrichment p38, JNK, NF-κB and MMP signaling pathways in human
44
45
of MF yielded transmembrane receptor protein kinase aortic smooth muscle cells. In the study by Oh et al.,
activity and glycosaminoglycan binding, and nuclear BO inhibited the synthesis and release of NO, iNOS,
receptor activity, and the involved targets mainly and pro-inflammatory factors by blocking ERK1/2 and
encompass TGFBR2, FGFR1, and FGFR2. Overall, these NF-κB in BV-2 microglias. These findings shed light
findings illuminate the complexity of ESCC pathology. To on an underlying mechanism for the anticancer effects
further examine the underlying mechanism by which BO of BO.
acts on ESCC, we performed KEGG analysis on the targets For the sake of further exploring the potential
and found that BO inhibited ESCC-related pathways, such mechanism of BO in inhibiting ESCC, we carried out
as MAPK signaling pathway, RAS signaling pathway, and a molecular docking study on AKT1, a closely related
Rap1 signaling pathway. target of ESCC, based on KEGG screening and using
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.2312