Page 106 - TD-3-3
P. 106
Tumor Discovery Effectiveness of AI imaging for lung nodules
Analyzing a large volume of CT images presents a cancer screening and diagnosis. Our project’s results
26
significant challenge, with the risk of missed diagnoses showed that the AI system achieved a sensitivity of 90.27%
due to the fatigue and mental stress associated with mass (95% CI: 0.8563 – 0.9380) in differentiating benign from
screening of high-risk groups. Therefore, accurately malignant lung nodules, which exceeds the sensitivity of
identifying high-risk nodules within a vast number of 83.19% (95% CI: 0.7766 – 0.8782) observed in physician
images has become an urgent clinical need. readings. The AI diagnostic imaging system demonstrated
Numerous studies have shown that AI diagnostic strong sensitivity in the qualitative diagnosis of lung
systems can outperform imaging physicians in detecting nodules, surpassing the physician-reading group. This
lung nodules. 33-36 Using precise algorithmic models, we result aligns with the 75.6% – 100% sensitivity range for AI
can rapidly detect lung nodules, perform qualitative reported in several studies. 33,37,38
analyses, and predict their benign or malignant nature. In the physician-reading group, nearly 40 pulmonary
This reduces subjective bias and enhances the efficiency nodules were not assessed for risk or categorized as
and objectivity of lung nodule analysis. Consequently, benign or malignant. This may be because radiologists
imaging physicians are partially relieved from the subjectively deemed the nodules at risk for malignancy,
repetitive and time-consuming task of nodule detection, despite the absence of typical malignant signs in the
allowing them to focus more on determining the images. This situation challenges clinicians in determining
malignancy of nodules. the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan for patients
Research indicates that applying AI to CT image with nodules. During pulmonary nodule follow-up,
recognition significantly improves the efficiency of lung dynamic changes in size or enlargement of the solid
component can help clinicians more accurately assess
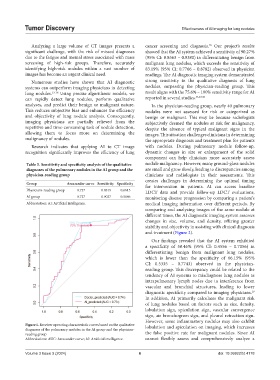
Table 5. Sensitivity and specificity analysis of the qualitative nodule malignancy. However, many ground-glass nodules
diagnoses of the pulmonary nodules in the AI group and the are small and grow slowly, leading to discrepancies among
physician‑reading group clinicians and radiologists in their assessments. This
creates challenges in determining the optimal timing
Group Area under curve Sensitivity Specificity for intervention in patients. AI can access baseline
Physicians-reading group 0.737 0.8319 0.6615 LDCT data and provide follow-up LDCT evaluations,
AI group 0.727 0.9027 0.5846 monitoring disease progression by comparing a patient’s
Abbreviation: AI: Artificial intelligence. medical imaging information over different periods. By
comparing and analyzing images of the same nodule at
different times, the AI diagnostic imaging system assesses
changes in size, volume, and density, offering greater
stability and objectivity in assisting with clinical diagnosis
and treatment (Figure 2).
Our findings revealed that the AI system exhibited
a specificity of 58.46% (95% CI: 0.4556 – 0.7056) in
differentiating benign from malignant lung nodules,
which is lower than the specificity of 66.15% (95%
CI: 0.5335 – 0.7743) observed in the physician-
reading group. This discrepancy could be related to the
tendency of AI systems to misdiagnose lung nodules as
intrapulmonary lymph nodes due to interference from
vascular and bronchial structures, leading to lower
diagnostic specificity compared to imaging physicians.
19
In addition, AI primarily calculates the malignant risk
of lung nodules based on factors such as size, density,
lobulation sign, spiculation sign, vascular convergence
sign, air bronchogram sign, and pleural retraction sign.
However, some inflammatory nodules may also exhibit
Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic curves based on the qualitative lobulation and spiculation on imaging, which increases
diagnoses of the pulmonary nodules in the AI group and the physician-
reading group the false positive rate for malignant nodules. Since AI
Abbreviations: AUC: Area under curve; AI: Artificial intelligence. cannot flexibly assess and comprehensively analyze a
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/td.4178