Page 107 - TD-3-3
P. 107
Tumor Discovery Effectiveness of AI imaging for lung nodules
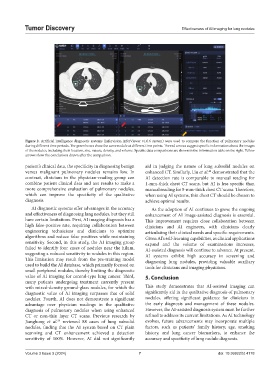
Figure 2. Artificial intelligence diagnostic systems (Infervision InferViewer v1.0.6 system) were used to compare the function of pulmonary nodules
during different time periods. The green boxes show the same nodule at different time points. The red arrows suggest specific information about the images
of the nodules, including their location, size, nature, density, and volume. Specific data comparisons are shown in the information table on the right. Yellow
arrows show the conclusions drawn after the comparison.
patient’s clinical data, the specificity in diagnosing benign aid in judging the nature of lung subsolid nodules on
versus malignant pulmonary nodules remains low. In enhanced CT. Similarly, Liu et al. demonstrated that the
40
contrast, clinicians in the physician-reading group can AI detection rate is comparable to manual reading for
combine patient clinical data and test results to make a 1-mm-thick chest CT scans, but AI is less specific than
more comprehensive evaluation of pulmonary nodules, manual reading for 5-mm-thick chest CT scans. Therefore,
which can improve the specificity of the qualitative when using AI systems, thin chest CT should be chosen to
diagnosis. achieve optimal results.
AI diagnostic systems offer advantages in the accuracy As the adoption of AI continues to grow, the ongoing
and effectiveness of diagnosing lung nodules, but they still enhancement of AI image-assisted diagnosis is essential.
have certain limitations. First, AI imaging diagnosis has a This improvement requires close collaboration between
high false-positive rate, requiring collaboration between clinicians and AI engineers, with clinicians clearly
engineering technicians and clinicians to optimize articulating their clinical needs and specific requirements.
algorithms and reduce false positives while maintaining Given AI’s self-learning capabilities, as clinical applications
sensitivity. Second, in this study, the AI imaging group expand and the volume of examinations increases,
failed to identify four cases of nodules near the hilum, AI-assisted diagnosis will continue to advance. At present,
suggesting a reduced sensitivity to nodules in this region. AI systems exhibit high accuracy in screening and
This limitation may result from the pre-training model diagnosing lung nodules, providing valuable auxiliary
used to build the AI database, which primarily focused on tools for clinicians and imaging physicians.
small peripheral nodules, thereby limiting the diagnostic
value of AI imaging for central-type lung cancer. Third, 5. Conclusion
many patients undergoing treatment currently present
with mixed-density ground-glass nodules, for which the This study demonstrates that AI-assisted imaging can
diagnostic value of AI imaging surpasses that of solid significantly aid in the qualitative diagnosis of pulmonary
nodules. Fourth, AI does not demonstrate a significant nodules, offering significant guidance for clinicians in
advantage over physician readings in the qualitative the early diagnosis and management of these nodules.
diagnosis of pulmonary nodules when using enhanced However, the AI-assisted diagnosis system must be further
CT or non-thin layer CT scans. Previous research by refined to address its current limitations. As AI technology
Jianghong et al. reviewed 88 cases of lung subsolid evolves, future advancements may incorporate multiple
39
nodules, finding that the AI system based on CT plain factors, such as patients’ family history, age, smoking
scanning and CT enhancement achieved a detection history, and lung cancer biomarkers, to enhance the
sensitivity of 100%. However, AI did not significantly accuracy and specificity of lung nodule diagnosis.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/td.4178