Page 47 - TD-3-4
P. 47
Tumor Discovery PPAR agonist and cancer
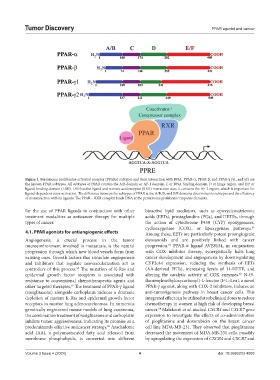
Figure 1. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARs) subtypes and their interaction with DNA. PPAR-α, PPAR-β, and PPAR-γ (γ1, and γ2) are
the known PPAR subtypes. All subtypes of PPAR contain the A/B domain or AF-1 domain, C or DNA binding domain, D or hinge region, and E/F or
ligand-binding domain (LBD). LBD has the ligand and retinoic acid receptor (RXR) interaction sites. It contains the AF-2 region, which is important for
ligand-dependent trans-activation. The difference between the subtypes of PPAR at the A/B, D, and E/F domains determines its subtypes and the efficiency
of its interaction with its ligands. The PPAR – RXR complex binds DNA at the peroxisome proliferator response elements.
for the use of PPAR ligands in conjunction with other bioactive lipid mediators, such as epoxyeicosatrienoic
treatment modalities as anticancer therapy for multiple acids (EETs), prostaglandins (PGs), and HETEs, through
types of cancer. the action of cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases,
cyclooxygenase (COX), or lipoxygenase pathways.
61
4.1. PPAR agonists for antiangiogenic effects Among these, EETs are particularly potent proangiogenic
Angiogenesis, a crucial process in the tumor eicosanoids and are positively linked with cancer
62
microenvironment involved in metastasis, is the natural progression. PPAR-α ligand AVE8134, in conjunction
progression through which new blood vessels form from with COX inhibitor therapy, synergistically halts lung
existing ones. Growth factors that stimulate angiogenesis cancer development and angiogenesis by downregulating
and inhibitors that regulate neovascularization act as CYP2c44 expression, reducing the synthesis of EETs
controllers of this process. The mutation of K-Ras and (AA-derived EETs), increasing levels of 11-HETE, and
58
epidermal growth factor receptors is associated with altering the catalytic activity of COX enzymes. N-(9-
63
resistance to conventional chemotherapeutic agents and fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl)-L-leucine (F-L-Leu), a novel
other targeted therapies. The treatment of PPAR-γ ligand PPAR-γ agonist, along with COX-2 inhibitors, induces an
59
(rosiglitazone) alongside carboplatin induces a dramatic anti-tumorigenesis pathway in breast cancer cells. This
depletion of mutant K-Ras and epidermal growth factor integrated effect can be utilized at subclinical doses to reduce
receptors in murine lung adenocarcinomas. In numerous chemotherapy in women at high risk of developing breast
genetically engineered mouse models of lung carcinoma, cancer. Malakouti et al. studied CXCR4 and CXCR7 gene
64
the combination treatment of rosiglitazone and carboplatin expression to investigate the effects of co-administration
inhibits tumor aggressiveness, indicating its promise as a of pioglitazone and doxorubicin on the breast cancer
predominantly effective anticancer strategy. Arachidonic cell line MDA-MB-231. They observed that pioglitazone
60
acid (AA), a polyunsaturated fatty acid released from decreased the movement of MDA-MB-231 cells, possibly
membrane phospholipids, is converted into different by upregulating the expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7 and
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/td.4003