Page 51 - TD-3-4
P. 51
Tumor Discovery PPAR agonist and cancer
the ROS scavenger N-acetylcysteine inhibited ROS levels and its transcriptional activity in ovarian cancer
production and the apoptotic cell death induced by this cells. 91
combination treatment. The synergistic treatment of Combination therapy using tumor necrosis factor-
87
TGZ and heregulin increased the generation of superoxide related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) with PPAR
in mitochondria, which disrupted mitochondrial potential ligands may offer a promising experimental approach, as
and induced substantial cell death in breast cancer cells. 88 PPAR ligands – particularly d15-PGJ2 – sensitize drug-
92
4.5. PPAR agonists for suppression of multidrug resistant ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
resistance (MDR) In general, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is upregulated during
inflammatory processes and oxidative stress in many
MDR is an acquired resistance that poses a major barrier to cancers, whereas PPAR-γ is typically downregulated in
the successful treatment of cancer. One of the most common these contexts. Therefore, PPAR-γ ligands have been
causes of MDR is the overexpression of P-glycoprotein shown to prevent cancer development by modulating the
(P-gp), which is encoded by the MDR1 gene. This gene Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. 93
is a direct target of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway,
which plays a key role in cancer progression. The effects 4.6. PPAR agonists in clinical trials for cancer
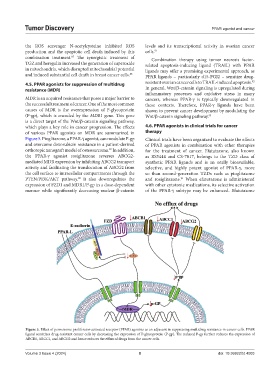
of various PPAR agonists on MDR are summarized in therapy
Figure 5. Pioglitazone, a PPAR-γ agonist, can modulate P-gp Clinical trials have been organized to evaluate the effects
and overcome doxorubicin resistance in a patient-derived of PPAR agonists in combination with other therapies
orthotopic xenograft model of osteosarcoma. In addition, for the treatment of cancer. Efatutazone, also known
89
the PPAR-γ agonist rosiglitazone reverses ABCG2- as RS5444 and CS-7017, belongs to the TZD class of
mediated MDR expression by inhibiting ABCG2 transport synthetic PPAR ligands and is an orally bioavailable,
activity and facilitating the translocation of ABCG2 from selective, and highly potent agonist of PPAR-γ, more
the cell surface to intracellular compartments through the so than second-generation TZDs such as pioglitazone
PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. It also downregulates the and rosiglitazone. When efatutazone is administered
94
90
expression of FZD1 and MDR1/P-gp in a dose-dependent with other cytotoxic medications, its selective activation
manner while significantly decreasing nuclear β-catenin of the PPAR-γ subtype may be enhanced. Efatutazone
Figure 5. Effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists as an adjuvant in suppressing multidrug resistance in cancer cells. PPAR
ligand sensitizes drug-resistant cancer cells by decreasing the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). The reduced P-gp further reduces the expression of
ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2 and hence reduces the efflux of drugs from the cancer cells.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/td.4003