Page 64 - TD-4-1
P. 64
Tumor Discovery Drug repurposing for pancreatic cancer via AI
K a denotes the a-th row of the matrix K; V b indicates the mechanisms of PDAC. Based on these insights, we
b-th principal singular vector; P 2− norm (a) represents the identified key biomarkers, listed in Table 1, which may
square root of the sum of the squared projection values serve as potential drug targets for drug repurposing to
of the a-th node onto the first J singular vectors, reflecting treat PDAC.
the significance of the node within the real GWGEN from
the network energy perspective. 2.6. Predicting drug candidates using deep neural
network-based drug-target interaction model and
Using the 2-norm projection value P 2− norm (a), we screening by design specifications for treating PDAC
extracted the top 6,000 ranked nodes, which we classified
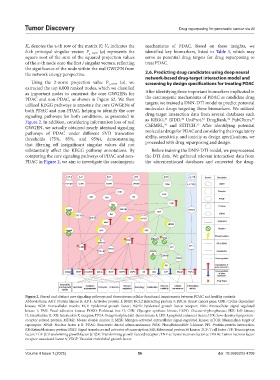
as important nodes to construct the core GWGENs for After identifying three important biomarkers implicated in
PDAC and non-PDAC, as shown in Figure S2. We then the carcinogenic mechanisms of PDAC as candidate drug
utilized KEGG pathways to annotate the core GWGENs of targets, we trained a DNN-DTI model to predict potential
both PDAC and non-PDAC, helping to identify the core molecular drugs targeting these biomarkers. We utilized
signaling pathways for both conditions, as presented in drug-target interaction data from several databases such
35
34
33
32
31
Figure 2. In addition, considering information loss of real as KEGG, BIDD, UniProt, DrugBank, PubChem,
36
37
GWGEN, we actually obtained nearly identical signaling ChEMBL, and STITCH. After identifying potential
pathways of PDAC under different SVD truncation molecular drugs for PDAC and considering their regulatory
thresholds (75%, 85%, and 95%), demonstrating ability, sensitivity, and toxicity as design specifications, we
that filtering off insignificant singular values did not proceeded with drug repurposing and design.
substantially affect the KEGG pathway annotations. By Before training the DNN-DTI model, we preprocessed
comparing the core signaling pathways of PDAC and non- the DTI data. We gathered relevant interaction data from
PDAC in Figure 2, we aim to investigate the carcinogenic the aforementioned databases and converted the drug-
Figure 2. Shared and distinct core signaling pathways and downstream cellular functional impairments between PDAC and healthy controls
Abbreviations: AKT: Protein kinase B; AP-1: Activator protein 1; BNIP: BCL2 interacting protein 3; BRCA: Breast cancer gene; CDK: Cyclin-dependent
kinase; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; FOXO: Forkhead box O; GSK: Glycogen synthase kinase; G6PC: Glucose-6-phosphatase; IKK: IκB kinase;
IL: Interleukin; IL-XR: Interleukin X receptor; ITGA: Integrin alpha; Jak1: Janus kinase 1; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer factor; LPR: Low-density-lipoprotein-
receptor-related-protein; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2; MEK: Mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of
rapamycin; NFκB: Nuclear factor κ B; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PPI: Protein-protein interaction;
RB: Retinoblastoma protein; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; S6K: Ribosomal protein S6 kinase; TCF: T cell factor; TF: Transcription
factor; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor β; TβR: Transforming growth factor β receptor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor
receptor-associated factor 6; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 56 doi: 10.36922/td.4709