Page 30 - TD-4-2
P. 30
Tumor Discovery Understanding glioblastoma invasion and therapy
A
B
C
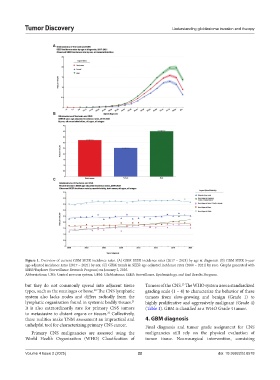
Figure 1. Overview of current GBM SEER incidence rates. (A) GBM SEER incidence rates (2017 – 2021) by age at diagnosis. (B) GBM SEER 5-year
age-adjusted incidence rates (2017 – 2021) by sex. (C) GBM trends in SEER age-adjusted incidence rates (2000 – 2021) by race. Graphs generated with
SEER*Explorer (Surveillance Research Program) on January 2, 2025.
Abbreviations: CNS: Central nervous system; GBM: Glioblastoma; SEER: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
but they do not commonly spread into adjacent tissue Tumors of the CNS. The WHO system uses a standardized
23
types, such as the meninges or bone. The CNS lymphatic grading scale (1 – 4) to characterize the behavior of these
20
system also lacks nodes and differs radically from the tumors from slow-growing and benign (Grade 1) to
lymphatic organization found in systemic bodily tissues. highly proliferative and aggressively malignant (Grade 4)
21
It is also extraordinarily rare for primary CNS tumors (Table 1). GBM is classified as a WHO Grade 4 tumor.
to metastasize to distant organs or tissues. Collectively,
22
these realities make TNM assessment an impractical and 4. GBM diagnosis
unhelpful tool for characterizing primary CNS cancer. Final diagnosis and tumor grade assignment for CNS
Primary CNS malignancies are assessed using the malignancies still rely on the physical evaluation of
World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of tumor tissue. Neurosurgical intervention, consisting
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 22 doi: 10.36922/td.8578