Page 32 - TD-4-2
P. 32
Tumor Discovery Understanding glioblastoma invasion and therapy
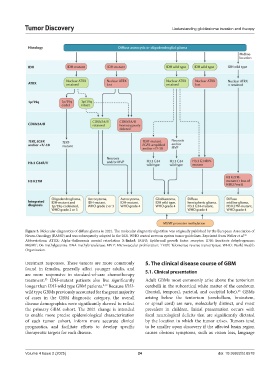
Figure 3. Molecular diagnostics of diffuse glioma in 2021. The molecular diagnostic algorithm was originally published by the European Association of
Neuro-Oncology (EANO) and was subsequently adopted in the 2021 WHO central nervous system tumor guidelines. Reprinted from Weller et al. 30
Abbreviations: ATRX: Alpha-thalassemia mental retardation X-linked; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; IDH: Isocitrate dehydrogenase;
MGMT: O6‑methylguanine‑DNA methyltransferase; MVP: Microvascular proliferation; TERT: Telomerase reverse transcriptase; WHO: World Health
Organization.
treatment responses. These tumors are more commonly 5. The clinical disease course of GBM
found in females, generally affect younger adults, and
are more responsive to standard-of-care chemotherapy 5.1. Clinical presentation
treatment. IDH-mutant patients also live significantly Adult GBMs most commonly arise above the tentorium
33
longer than IDH-wild type GBM patients. Because IDH- cerebelli in the subcortical white matter of the cerebrum
8,12
25
wild type GBMs previously accounted for the great majority (frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobe). GBMs
of cases in the GBM diagnostic category, the overall arising below the tentorium (cerebellum, brainstem,
disease demographics were significantly skewed to reflect or spinal cord) are rare, molecularly distinct, and most
the primary GBM cohort. The 2021 change is intended prevalent in children. Initial presentation occurs with
to enable more precise epidemiological characterization focal neurological deficits that are significantly dictated
of each tumor cohort, inform more accurate clinical by the location in which the tumor arises. Tumors tend
prognostics, and facilitate efforts to develop specific to be smaller upon discovery if the affected brain region
therapeutic targets for each disease. causes obvious symptoms, such as vision loss, language
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 24 doi: 10.36922/td.8578