Page 36 - TD-4-2
P. 36
Tumor Discovery Understanding glioblastoma invasion and therapy
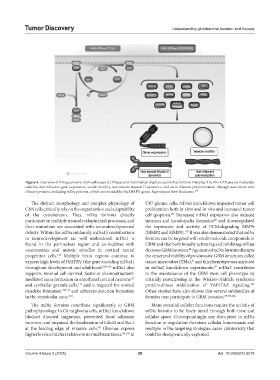
Figure 4. Overview of Rho guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) and mammalian diaphanous (mDia) formins interplay. The Rho GTPases are molecular
switches that influence gene expression, vesicle motility, non-muscle myosin II dynamics, and actin filament polymerization through association with
effector proteins, including mDia proteins, which are encoded by the DIAPH genes. Reproduced from Reactome. 109
The distinct morphology and complex physiology of U87 glioma cells, mDia1 knockdown impaired tumor cell
CNS cells critically rely on the organization and adaptability proliferation both in vitro and in vivo and increased tumor
of the cytoskeleton. Thus, mDia formins directly cell apoptosis. Decreased mDia1 expression also reduced
86
participate in multiple neurodevelopmental processes, and invasion and invadopodia formation and downregulated
86
their mutations are associated with neurodevelopmental the expression and activity of ECM-degrading MMPs
defects. Within the mDia subfamily, mDia1’s contributions (MMP2 and MMP9). It was also demonstrated that mDia
120
to neurodevelopment are well understood. mDia1 is formins can be targeted with small-molecule compounds in
found in the perinuclear region and co-localizes with GBM and that both broadly activating and inhibiting mDias
centrosomes and mitotic spindles in cortical neural decrease GBM invasion. Agonism of mDia formins disrupts
84
progenitor cells. Multiple brain regions continue to the structural viability of pro-invasive GBM structures called
113
express high levels of DIAPH1 (the gene encoding mDia1) tumor microtubes (TMs), and this phenotype was mirrored
91
throughout development and adulthood. 114-116 mDia1 also in mDia2 knockdown experiments. mDia2 contributes
87
supports stromal cell-derived factor-α chemoattractant- to the maintenance of the GBM stem cell phenotype by
mediated axon formation in entorhinal cortical neurons critically participating in the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome
117
and cerebellar granule cells, and is required for normal protein-driven stabilization of YAP/TAZ signaling.
114
121
dendrite formation 118,119 and adherens junction formation Other studies have also shown that several subfamilies of
in the ventricular zone. 115 formins may participate in GBM invasion. 87-89,122
The mDia formins contribute significantly to GBM Many essential cellular functions require the activity of
pathophysiology. In C6 rat glioma cells, mDia1 knockdown mDia formins to be finely tuned through both time and
blocked directed migration, prevented focal adhesion cellular space. Correspondingly, any disruption to mDia
turnover, and impaired the localization of Cdc42 and Rac1 function or regulation threatens cellular homeostasis and
at the leading edge of invasive cells. Gliomas express multiple mDia-targeting strategies cause cytotoxicity that
85
higher levels of mDia1 relative to normal brain tissue. 86,120 In could be therapeutically exploited.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 28 doi: 10.36922/td.8578