Page 110 - TD-4-3
P. 110
Tumor Discovery Mature teratoma during pregnancy
A B C
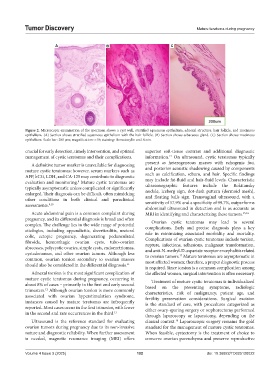
Figure 2. Microscopic examination of the specimen shows a cyst wall, stratified squamous epithelium, adnexal structure, hair follicle, and mucinous
epithelium. (A) Section shows stratified squamous epithelium with the hair follicle. (B) Section shows sebaceous gland. (C) Section shows mucinous
epithelium. Scale bar: 200 µm; magnification: ×10; staining: Hematoxylin and Eosin.
crucial for early detection, timely intervention, and optimal superior soft-tissue contrast and additional diagnostic
management of cystic teratomas and their complications. information. On ultrasound, cystic teratomas typically
14
A definitive tumor marker is unavailable for diagnosing present as heterogeneous masses with echogenic foci
mature cystic teratomas; however, serum markers such as and posterior acoustic shadowing caused by components
AFP, hCG, LDH, and CA-125 may contribute to diagnostic such as calcification, sebum, and hair. Specific findings
evaluation and monitoring. Mature cystic teratomas are may include fat-fluid and hair-fluid levels. Characteristic
8
ultrasonographic features include the Rokitansky
typically asymptomatic unless complicated or significantly
enlarged. Their diagnosis can be difficult, often mimicking nodule, iceberg sign, dot-dash pattern (dermoid mesh),
other conditions in both clinical and paraclinical and floating balls sign. Transvaginal ultrasound, with a
assessments. 9,10 sensitivity of 57.9% and a specificity of 99.7%, outperforms
abdominal ultrasound in detection and is as accurate as
Acute abdominal pain is a common complaint during MRI in identifying and characterizing these tumors. 15,16
pregnancy, and its differential diagnosis is broad and often Ovarian cystic teratomas may lead to several
complex. The challenge lies in the wide range of potential complications. Early and precise diagnosis plays a key
etiologies, including appendicitis, diverticulitis, ureteral role in minimizing associated morbidity and mortality.
colic, ectopic pregnancy, degenerating pedunculated
fibroids, hemorrhagic ovarian cysts, tubo-ovarian Complications of ovarian cystic teratomas include torsion,
rupture, infections, adhesions, malignant transformation,
abscesses, polycystic ovaries, simple cysts, endometriomas, and anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis related
cystadenomas, and other ovarian tumors. Although less to ovarian tumors. Mature teratomas are asymptomatic in
17
common, ovarian torsion secondary to ovarian masses most affected women; therefore, a proper diagnostic process
should also be considered in the differential diagnosis. 11
is required. Since torsion is a common complication among
Adnexal torsion is the most significant complication of the affected women, surgical intervention is often necessary.
mature cystic teratomas during pregnancy, occurring in Treatment of mature cystic teratomas is individualized
about 8% of cases – primarily in the first and early second based on the presenting symptoms, radiologic
trimesters. Although ovarian torsion is more commonly characteristics, risk of malignancy, patient age, and
12
associated with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, fertility preservation considerations. Surgical excision
instances caused by mature teratomas are infrequently is the standard of care, with procedures categorized as
reported. Most cases occur in the first trimester, with fewer either ovary-sparing surgery or oophorectomy performed
in the second and rare occurrences in the third. 13 through laparoscopy or laparotomy, depending on the
Ultrasound is the reference standard for evaluating clinical context. Laparoscopic surgery remains the gold
18
ovarian tumors during pregnancy due to its non-invasive standard for the management of mature cystic teratomas.
nature and diagnostic reliability. When further assessment When feasible, cystectomy is the treatment of choice to
is needed, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers conserve ovarian parenchyma and preserve reproductive
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 102 doi: 10.36922/TD025120022