Page 62 - manuscript_ijb05590
P. 62
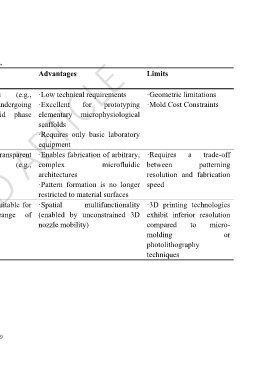
Table 2. Summary of preparation methods for microfluidic devices.
Microfluidic Principle Materials Advantages Limits
fabrication techniques
Micro-molding Microfluidic channels are Biomaterials (e.g., ·Low technical requirements ·Geometric limitations
formed by molding hydrogels) undergoing ·Excellent for prototyping ·Mold Cost Constraints
biomaterials onto pre- liquid-to-solid phase elementary microphysiological
patterned templates, followed transition scaffolds
by template removal ·Requires only basic laboratory
equipment
Photolithography Light-directed microchannel Optically transparent ·Enables fabrication of arbitrary, ·Requires a trade-off
fabrication via materials (e.g., complex microfluidic between patterning
photodegradation or hydrogels) architectures resolution and fabrication
photopolymerization ·Pattern formation is no longer speed
patterning restricted to material surfaces
3D printing Direct fabrication of Universal, suitable for ·Spatial multifunctionality ·3D printing technologies
microfluidic channels via 3D a wide range of (enabled by unconstrained 3D exhibit inferior resolution
printing materials nozzle mobility) compared to micro-
molding or
photolithography
techniques
59