Page 65 - manuscript_ijb05590
P. 65
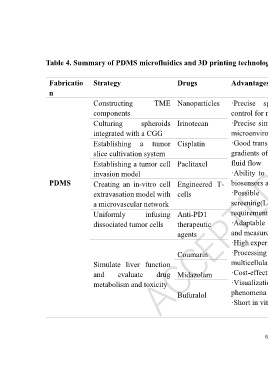
Table 4. Summary of PDMS microfluidics and 3D printing technology in tumor therapy research
Fabricatio Strategy Drugs Advantages Disadvantages Reference
n
81
Constructing TME Nanoparticles ·Precise spatial and temporal ·Difficult to scale up Oh et al.
components control for microenvironment ·No standardized
Culturing spheroids Irinotecan ·Precise simulation of the in vivo protocol 82
integrated with a CGG microenvironment ·More complex in Lim and Park
Establishing a tumor Cisplatin ·Good transport and concentration operation 83
slice cultivation system gradients of nutrient and drugs by ·Require external Komar et al.
Establishing a tumor cell Paclitaxel fluid flow equipment 84
invasion model ·Ability to integrate with various ·High chance of Du et al.
PDMS Creating an in-vitro cell Engineered T- biosensors and mechanical stimuli contamination
85
extravasation model with cells ·Possible for high-throughput ·Laborious process Pavesi et al.
a microvascular network screening(Low sample volume of chip fabrication
Uniformly infusing Anti-PD1 requirement) ·Closed-system
71
dissociated tumor cells therapeutic ·Adaptable for real-time imaging design of CoC Ao et al.
agents and measurements devices restricted
·High experimental reproducibility utility for culturing
Coumarin ·Processing and routine analysis of larger tissue
86
Simulate liver function multicellular spheroids specimens Sano et al.
and evaluate drug Midazolam ·Cost-effective ·High absorptivity of
metabolism and toxicity ·Visualization of in-vitro complex hydrophobic small-
Bufuralol phenomena with high resolution molecule drugs,
·Short in vitro culture time leading to significant
alterations in
61