Page 107 - AIH-1-3
P. 107
Artificial Intelligence in Health ISM: A new multi-view space-learning model
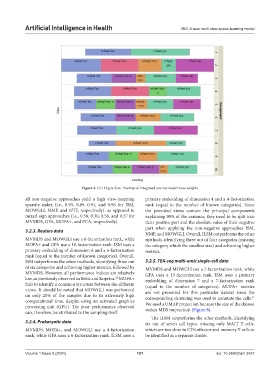
Figure 4. UCI Digits data: Treemap of integrated sources model view weights
all non-negative approaches yield a high view-mapping primary embedding of dimension 4 and a 4-factorization
sparsity index (i.e., 0.93, 0.89, 0.91, and 0.98 for ISM, rank (equal to the number of known categories). Since
MOWGLI, NMF, and NTF, respectively), as opposed to the provided views contain the principal components
mixed-sign approaches (i.e., 0.56, 0.30, 0.56, and 0.57 for explaining 90% of the variance, they need to be split into
MVMDS, GFA, MOFA+, and PCA, respectively). their positive part and the absolute value of their negative
part when applying the non-negative approaches ISM,
3.2.3. Reuters data
NMF, and MOWGLI. Overall, ILSM outperforms the other
MVMDS and MOWGLI use a 6-factorization rank, while methods, identifying three out of four categories (missing
MOFA+ and GFA use a 10-factorization rank. ISM uses a the category which the smallest size) and achieving higher
primary embedding of dimension 6 and a 6-factorization metrics.
rank (equal to the number of known categories). Overall,
ISM outperforms the other methods, identifying three out 3.2.5. TEA-seq multi-omic single-cell data
of six categories and achieving higher metrics, followed by MVMDS and MOWGLI use a 7-factorization rank, while
MVMDS. However, all performance indices are relatively GFA uses a 15-factorization rank. ISM uses a primary
low, as previously observed in Brbic and Kopriva. MOFA+ embedding of dimension 7 and a 7-factorization rank
22
fails to identify a common structure between the different (equal to the number of categories). MOFA+ metrics
views. It should be noted that MOWGLI was performed are not presented for this particular dataset since the
on only 20% of the samples due to its extremely high corresponding clustering was used to annotate the cells.
21
computational time, despite using an activated graphics We used a UMAP projection because the size of the dataset
processing unit (GPU). The poor performance observed
can, therefore, be attributed to the sampling itself. makes MDS impractical (Figure 8).
The ILSM outperforms the other methods, identifying
3.2.4. Prokaryotic data six out of seven cell types, missing only MAIT T cells,
MVMDS, MOFA+, and MOWGLI use a 4-factorization which are too close to CD4 effector and memory T cells to
rank, while GFA uses a 6-factorization rank. ILSM uses a be identified as a separate cluster.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 101 doi: 10.36922/aih.3427