Page 111 - AIH-1-3
P. 111
Artificial Intelligence in Health ISM: A new multi-view space-learning model
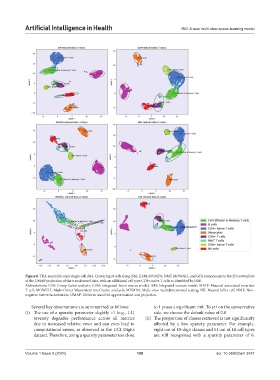
Figure 8. TEA-seq multi-omic single-cell data: Clustering of cells along ISM, ILSM, MVMDS, NMF, MOWGLI, and GFA components in the 2D scatterplots
of the UMAP projection of the transformed data, with an additional cell type CD8+ naïve T cells as identified by ISM.
Abbreviations: GFA: Group factor analysis; ILSM: Integrated latent source model; ISM: Integrated sources model; MAIT: Mucosal-associated invariant
T cell; MOWGLI: Multi-Omics Wasserstein inteGrative anaLysIs; MVMDS: Multi-view multidimensional scaling; NK: Natural killer cell; NMF: Non-
negative matrix factorization; UMAP: Uniform manifold approximation and projection.
Several key observations are summarized as follows: to 1 poses a significant risk. To err on the conservative
(i) The use of a sparsity parameter slightly >1 (e.g., 1.1) side, we choose the default value of 0.8.
severely degrades performance across all metrics (ii) The proportion of classes retrieved is not significantly
due to increased relative error and can even lead to affected by a low sparsity parameter. For example,
computational errors, as observed in the UCI Digits eight out of 10-digit classes and 11 out of 16 cell types
dataset. Therefore, using a sparsity parameter too close are still recognized with a sparsity parameter of 0.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 105 doi: 10.36922/aih.3427