Page 127 - AIH-1-3
P. 127
Artificial Intelligence in Health Interpretability of deep models for COVID-19
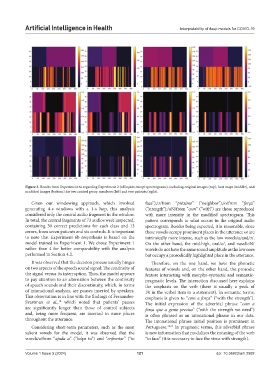
Figure 3. Results from Experiment 6a regarding Experiment 2 (all inputs except spectrograms), including original images (top), heat maps (middle), and
modified images (bottom) for two control group members (left) and two patients (right).
Given our windowing approach, which involved face”);/ɔ/from “próximo” (“neighbor”);/o/from “força”
generating 4-s windows with a 1-s hop, this analysis (“strength”);/oN/from “com” (“with”) are those reproduced
considered only the central audio fragment in the window. with more intensity in the modified spectrogram. This
In total, the central fragments of 73 audios were inspected, pattern corresponds to what occurs in the original audio
containing 30 correct predictions for each class and 13 spectrogram. Besides being expected, it is reasonable, since
errors, from seven patients and six controls. It is important these vowels occupy prominent places in the utterance or are
to note that Experiment 6b resynthesis is based on the intrinsically more intense, such as the low vowels/a/and/ɔ/.
model trained in Experiment 1. We chose Experiment 1 On the other hand, the mid-high, oral/o/, and nasal/oN/
rather than 4 for better comparability with the analysis vowels do not have the same sound amplitude as the low ones
performed in Section 4.2. but occupy a prosodically highlighted place in the utterance.
It was observed that the decision process usually hinges Therefore, on the one hand, we have the phonetic
on two aspects of the speech sound signal: The continuity of features of vowels and, on the other hand, the prosodic
the signal versus its interruption. Thus, the model appears feature interacting with morpho-syntactic and semantic-
to pay attention to an alternation between the continuity pragmatic levels. The interaction discussed here explains
of speech sounds and their discontinuity, which, in terms the emphasis on the verb (there is usually a peak of
of intonational analysis, are pauses inserted by speakers. F0 in the verbal item in a statement). In semantic terms,
This observation is in line with the findings of Fernandes- emphasis is given to “com a força” (“with the strength”).
Svartman et al., which noted that patients’ pauses The initial expression of the adverbial phrase “com a
18
are significantly longer than those of control subjects força que a gente precisa” (“with the strength we need”)
and, being more frequent, are inserted in more places is often phrased as an intonational phrase in our data.
throughout the utterance. The intonational phrase initial position is prominent in
Considering short-term parameters, such as the most Portuguese. 32,33 In pragmatic terms, this adverbial phrase
salient vowels for the model, it was observed that the is new information that modalizes the meaning of the verb
vowels/a/from “ajuda a” (“helps to”) and “enfrentar” (“to “to face” (it is necessary to face the virus with strength).
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 121 doi: 10.36922/aih.2992