Page 116 - AIH-1-4
P. 116
Artificial Intelligence in Health Complex early diagnosis of MS through machine learning
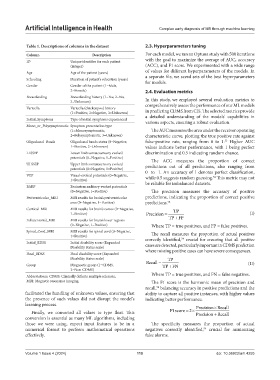
Table 1. Descriptions of columns in the dataset 2.3. Hyperparameters tuning
Column Description For each model, we ran an Optuna study with 500 iterations
ID Unique identifier for each patient with the goal to maximize the average of AUC, accuracy
(integer) (ACC), and F1 score. We experimented with a wide range
Age Age of the patient (years) of values for different hyperparameters of the models. In
Schooling Duration of patient’s education (years) a separate file, we saved sets of the best hyperparameters
for models.
Gender Gender of the patient (1=Male,
2=Female) 2.4. Evaluation metrics
Breastfeeding Breastfeeding history (1=Yes, 2=No, In this study, we employed several evaluation metrics to
3=Unknown)
Varicella Varicella (chickenpox) history comprehensively assess the performance of our ML models
(1=Positive, 2=Negative, 3=Unknown) in predicting CDMS from CIS. The selected metrics provide
Initial_Symptoms Type of initial symptoms experienced a detailed understanding of the models’ capabilities in
various aspects, ensuring a robust evaluation.
Mono_or_Polysymptomatic Symptom presentation type
(1=Monosymptomatic, The AUC measures the area under the receiver operating
2=Polysymptomatic, 3=Unknown) characteristic curve, plotting the true positive rate against
53
Oligoclonal_Bands Oligoclonal bands status (0=Negative, false-positive rate, ranging from 0 to 1. Higher AUC
1=Positive, 2=Unknown) values indicate better performance, with 1 being perfect
LLSSEP Lower limb somatosensory evoked discrimination and 0.5 indicating random chance.
potentials (0=Negative, 1=Positive) The ACC measures the proportion of correct
ULSSEP Upper limb somatosensory evoked predictions out of all predictions, also ranging from
potentials (0=Negative, 1=Positive)
VEP Visual-evoked potentials (0=Negative, 0 to 1. An accuracy of 1 denotes perfect classification,
while 0.5 suggests random guessing. This metric may not
54
1=Positive)
BAEP Brainstem auditory-evoked potentials be reliable for imbalanced datasets.
(0=Negative, 1=Positive) The precision measures the accuracy of positive
Periventricular_MRI MRI results for brain’s periventricular predictions, indicating the proportion of correct positive
area (0=Negative, 1=Positive) predictions. 54
Cortical_MRI MRI results for brain’s cortex (0=Negative, TP
1=Positive) Precision (I)
Infratentorial_MRI MRI results for brain’s lower regions TP FP
(0=Negative, 1=Positive) Where TP = true positives, and FP = false positives.
Spinal_Cord_MRI MRI results for spinal cord (0=Negative, The recall measures the proportion of actual positives
1=Positive) 54
Initial_EDSS Initial disability score (Expanded correctly identified, crucial for ensuring that all positive
cases are detected, particularly important in CDMS prediction
Disability Status scale)
Final_EDSS Final disability score (Expanded where missing positive cases can have severe consequences.
Disability Status scale) TP
Group Diagnostic group (1=CDMS, Recall TP FN (II)
2=Non-CDMS)
Abbreviations: CDMS: Clinically definite multiple sclerosis; Where TP = true positives, and FN = false negatives.
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging. The F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and
recall, balancing accuracy in positive predictions and the
54
facilitated the handling of unknown values, ensuring that ability to capture all positive instances, with higher values
the presence of such values did not disrupt the model’s indicating better performance.
learning process. PrecisionRecall
2
Finally, we converted all values to type float. This Fscore1 PrecisionRecall
conversion is essential as many ML algorithms, including
those we were using, expect input features to be in a The specificity measures the proportion of actual
numerical format to perform mathematical operations negatives correctly identified, crucial for minimizing
54
effectively. false alarms.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 110 doi: 10.36922/aih.4255