Page 120 - AIH-1-4
P. 120
Artificial Intelligence in Health Complex early diagnosis of MS through machine learning
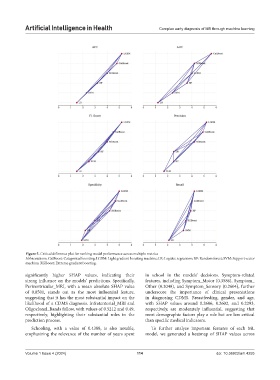
Figure 5. Critical difference plot for ranking model performance across multiple metrics
Abbreviations: CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LGBM: Light gradient boosting machine; LR: Logistic regression; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector
machine; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
significantly higher SHAP values, indicating their in school in the models’ decisions. Symptom-related
strong influence on the models’ predictions. Specifically, features, including Symptom_Motor (0.3586), Symptom_
Periventricular_MRI, with a mean absolute SHAP value Other (0.3048), and Symptom_Sensory (0.2604), further
of 0.8501, stands out as the most influential feature, underscore the importance of clinical presentations
suggesting that it has the most substantial impact on the in diagnosing CDMS. Breastfeeding, gender, and age,
likelihood of a CDMS diagnosis. Infratentorial_MRI and with SHAP values around 0.2606, 0.2602, and 0.2293,
Oligoclonal_Bands follow, with values of 0.5212 and 0.49, respectively, are moderately influential, suggesting that
respectively, highlighting their substantial roles in the most demographic factors play a role but are less critical
prediction process. than specific medical indicators.
Schooling, with a value of 0.4388, is also notable, To further analyze important features of each ML
emphasizing the relevance of the number of years spent model, we generated a heatmap of SHAP values across
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 114 doi: 10.36922/aih.4255