Page 119 - AIH-1-4
P. 119
Artificial Intelligence in Health Complex early diagnosis of MS through machine learning
in their ranks are not statistically significant, meaning they
perform similarly. The plot shows that CatBoost, LGBM,
and XGBoost consistently rank as top performers, with
minimal and statistically insignificant differences among
them, indicating their similar effectiveness. In contrast,
SVM and LR are consistently lower in the rankings,
confirming their comparatively weaker performance.
3.2. Feature importance analysis
To identify important features for CDMS diagnosis
prediction, we calculated mean absolute SHAP values of
features across six ML models over five validation folds,
then illustrated their rankings, as shown in Figure 6. We
observed that the presence or absence of lesions in brain
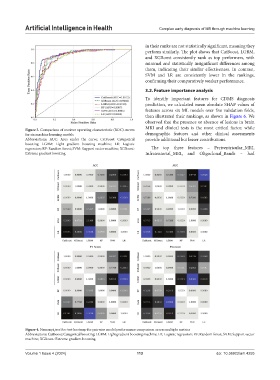
Figure 3. Comparison of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves MRI and clinical tests is the most critical factor, while
for six machine learning models demographic features and other clinical assessments
Abbreviations: AUC: Area under the curve; CatBoost: Categorical provide additional but lesser contributions.
boosting; LGBM: Light gradient boosting machine; LR: Logistic
regression; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector machine; XGBoost: The top three features – Periventricular_MRI,
Extreme gradient boosting. Infratentorial_MRI, and Oligoclonal_Bands – had
Figure 4. Nemenyi post hoc test heatmap for pairwise model performance comparison across multiple metrics
Abbreviations: CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LGBM: Light gradient boosting machine; LR: Logistic regression; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector
machine; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 113 doi: 10.36922/aih.4255