Page 118 - AIH-1-4
P. 118
Artificial Intelligence in Health Complex early diagnosis of MS through machine learning
CatBoost emerged as the top performer with an AUC of alarms is critical. Overall, CatBoost, XGBoost, and LGBM
0.9312, a balanced F1 score of 0.8675, precision of 0.8710, are the most reliable models for CDMS prediction, with
recall of 0.8640, and specificity of 0.8919, showcasing CatBoost excelling in sensitivity, reducing false negatives,
its effectiveness in both positive and negative case and ensuring accurate diagnoses.
identification. LGBM matched CatBoost closely in these
metrics, making it another strong classifier. XGBoost also 3.1.2. Statistical significance of model performance
performed well with an AUC of 0.9202 but showed slightly Figure 4 shows the Nemenyi post hoc test heatmap. It shows
less balanced precision and recall compared to CatBoost that CatBoost, LGBM, and XGBoost consistently ranked
and LGBM. RF, while having a solid AUC of 0.9097, as the best models. However, the differences between these
exhibited less balance in precision and recall, resulting in models were not statistically significant, as shown by higher
more false positives. P-values in most metrics. However, we observe significant
SVM and LR demonstrated lower performance overall. differences between these top models and the lower-
SVM’s AUC of 0.8985 and F1 score of 0.8031 indicated performing models, particularly LR and SVM. For instance,
moderate effectiveness but higher false-positive rates. LR P-values from the Nemenyi test showed that CatBoost did
had the lowest performance, with an AUC of 0.8922 and much better than LR in AUC, supporting earlier findings
the lowest balance between precision and recall, making it that gradient-boosted models are better at predicting
the least effective model evaluated. CDMS. This statistical validation underscores the reliability
of the gradient-boosted models, particularly CatBoost and
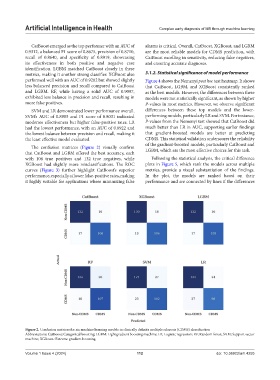
The confusion matrices (Figure 2) visually confirm
that CatBoost and LGBM offered the best accuracy, each LGBM, which are the most effective choices for this task.
with 108 true positives and 132 true negatives, while Following the statistical analysis, the critical difference
XGBoost had slightly more misclassifications. The ROC plots in Figure 5, which rank the models across multiple
curves (Figure 3) further highlight CatBoost’s superior metrics, provide a visual substantiation of the findings.
performance, especially at lower false-positive rates, making In the plot, the models are ranked based on their
it highly suitable for applications where minimizing false performance and are connected by lines if the differences
Figure 2. Confusion matrices for six machine learning models in clinically definite multiple sclerosis (CDMS) classification
Abbreviations: CatBoost: Categorical boosting; LGBM: Light gradient boosting machine; LR: Logistic regression; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector
machine; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 112 doi: 10.36922/aih.4255