Page 75 - AIH-1-4
P. 75
Artificial Intelligence in Health ML models for heartbeat classification
4. Discussion Table 3. Comparison between the proposed ML model
and state‑of‑art algorithms in terms of their accuracy
XGBoost, the best-performing classifier, was applied performance
to the test set to generate a confusion matrix, assessing
the effectiveness of the classification model. An overall Approach Overall accuracy (%)
accuracy of 99.96% demonstrated the model’s ability to Proposed approach 99.96
classify ECG signals more accurately than other MLmodels. ML models with Optimized RF 46 97.7
Table 3 highlights the superior performance of our method Deep LSTM 47 95.80
in efficiently and automatically identifying arrhythmias Deep 1D-CNN 48 97.00
through the classification of heartbeats from the ECG 17
signals. The accuracy of the proposed method with balanced CNN+LSTM 99.35
data surpasses that of other state-of-art methods, especially RC+NG-RC 44 96.05 and 98.28
for the N, S, and V categories (Table 1), achieving values Bi-LSTMs 49 98.70
of 99.96% and 95.68% for training and test, respectively.
These values represent greater performance than obtained
with other state-of-the-art methods that use the previously
proposed reservoir computing (RC) and next-generation
RC approaches. While a previous study achieved an
45
44
accuracy of 99.6% by introducing a CNN-based model
with feature component analysis for multimodal ECG
tasks on the MIT-BIH dataset, our model exhibits sound
performance by incorporating the FT and Gaussian noise
injection techniques. Another study explored heartbeat
17
classification and arrhythmia detection using multimodel
deep learning techniques such as a one-dimensional CNN
and long short-term memory network, achieving overall
accuracies of 99.59% and 99.35%, respectively, which are
lower than those achieved in our study, supporting the
reliability of our model in heartbeat classification. The
proposed approach also requires lesser training time and is
more cost-effective than other state-of-the-art algorithms,
which are often deemed expensive and time-consuming.
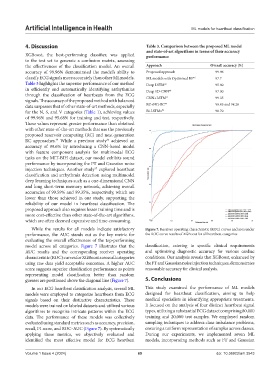
While the results for all models indicate satisfactory Figure 7. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and area under
performance, the AUC stands out as the key metric for the ROC curve results of XGBoost for all heartbeat categories
evaluating the overall effectiveness of the top-performing
model across all categories. Figure 7 illustrates that the classification, catering to specific clinical requirements
AUC results and the corresponding receiver operating and optimizing diagnostic accuracy for various cardiac
characteristic (ROC) curves for XGBoost across all categories conditions. Our analysis reveals that XGBoost, enhanced by
using raw data yield acceptable outcomes. A higher AUC the FT and Gaussian noise injection techniques, demonstrates
score suggests superior classification performance as points reasonable accuracy for clinical analysis.
representing model classification better than random
guesses are positioned above the diagonal line (Figure 7). 5. Conclusions
In our ECG heartbeat classification analysis, several ML This study examined the performance of ML models
models were employed to categorize heartbeats from ECG designed for heartbeat classification, aiming to help
signals based on their distinctive characteristics. These medical specialists in identifying appropriate treatments.
models were trained on labeled datasets and utilized various It focused on the analysis of four distinct heartbeat signal
algorithms to recognize intricate patterns within the ECG types, utilizing a substantial ECG dataset comprising 80,000
data. The performance of these models was collectively training and 20,000 test samples. We employed random
evaluated using standard metrics such as accuracy, precision, sampling techniques to address class imbalance problems,
recall, F1 score, and ROC‒AUC (Figure 7). By systematically ensuring a uniform representation of samples across classes.
applying these metrics, we objectively evaluated and During our experiments, we implemented seven ML
identified the most effective model for ECG heartbeat models, incorporating methods such as FT and Gaussian
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 69 doi: 10.36922/aih.3543