Page 69 - AIH-2-1
P. 69
Artificial Intelligence in Health Algorithm and metal oxide nanoparticle in MRI
A B
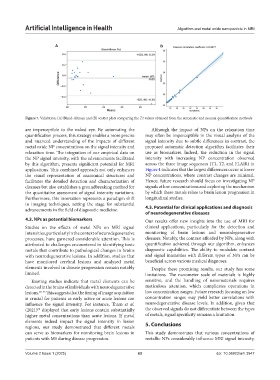
Figure 7. Validation. (A) Bland‒Altman and (B) scatter plots comparing the T1 values obtained from the automatic and manual quantification methods
are imperceptible to the naked eye. By automating the Although the impact of NPs on the relaxation time
quantification process, this strategy enables a more precise may often be imperceptible in the visual analysis of the
and nuanced understanding of the impacts of different signal intensity due to subtle differences in contrast, the
metal oxide NP concentrations on the signal intensity and proposed automatic detection algorithm facilitates their
relaxation time. The integration of our empirical data on use as biomarkers. Indeed, the reduction in the signal
the NP signal intensity, with the advancements facilitated intensity with increasing NP concentration observed
by this algorithm, presents significant potential for MRI across the three image sequences (T1, T2, and FLAIR) in
applications. This combined approach not only enhances Figure 4 indicates that the largest differences occur at lower
the visual representation of anatomical structures and NP concentrations, where contrast changes are minimal.
facilitates the detailed detection and characterization of Hence, future research should focus on investigating NP
diseases but also establishes a groundbreaking method for signals at low concentrations and exploring the mechanism
the quantitative assessment of signal intensity variations. by which these metals relate to brain lesion progression in
Furthermore, this innovation represents a paradigm shift longitudinal studies.
in imaging techniques, setting the stage for substantial
advancements in the field of diagnostic medicine. 4.3. Potential for clinical applications and diagnosis
of neurodegenerative diseases
4.2. NPs as potential biomarkers Our results offer new insights into the use of MRI for
Studies on the effects of metal NPs on MRI signal clinical applications, particularly for the detection and
intensities, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative monitoring of brain lesions and neurodegenerative
processes, have garnered considerable attention. This is diseases. Notably, the contrast afforded by NPs, along with
attributed to challenges encountered in identifying toxic quantification achieved through our algorithm, enhances
metals that contribute to pathological changes in brains diagnostic capabilities. The ability to modulate contrast
with neurodegenerative lesions. In addition, studies that and signal intensities with different types of NPs can be
have monitored cerebral lesions and analyzed metal beneficial across various medical diagnoses.
elements involved in disease progression remain notably Despite these promising results, our study has some
limited. limitations. The nanometer scale of materials is highly
Existing studies indicate that metal elements can be sensitive, and the handling of nanomaterials requires
detected in the brains of individuals with neurodegenerative meticulous attention, which complicates operations in
lesions. 69-73 This suggests that the timing of image acquisition low concentration ranges. Future research focusing on low
is crucial for patients as early active or acute lesions can concentration ranges may yield better correlations with
influence the signal intensity. For instance, Tham et al. neurodegenerative disease levels. In addition, given that
(2021) displayed that early lesions contain substantially the observed signals do not differentiate between the types
69
higher metal concentrations than acute lesions. If metal of metals, signal specificity remains a limitation.
elements indeed impact the signal intensity in lesion
regions, our study demonstrated that different metals 5. Conclusions
can serve as biomarkers for monitoring brain lesions in This study demonstrates that various concentrations of
patients with MS during disease progression. metallic NPs considerably influence MRI signal intensity,
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 63 doi: 10.36922/aih.3947