Page 67 - AIH-2-1
P. 67
Artificial Intelligence in Health Algorithm and metal oxide nanoparticle in MRI
A B
C D
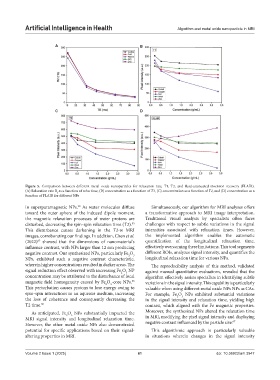
Figure 5. Comparison between different metal oxide nanoparticles for relaxation rate, T1, T2, and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR).
(A) Relaxation rate R as a function of echo time, (B) concentration as a function of T1, (C) concentration as a function of T2, and (D) concentration as a
2
function of FLAIR for different NPs
in superparamagnetic NPs. As water molecules diffuse Simultaneously, our algorithm for MRI analyses offers
20
toward the outer sphere of the induced dipole moment, a transformative approach to MRI image interpretation.
the magnetic relaxation processes of water protons are Traditional visual analysis by specialists often faces
disturbed, decreasing the spin‒spin relaxation time (T2). challenges with respect to subtle variations in the signal
53
This disturbance causes darkening in the T2-w MRI intensities associated with relaxation times. However,
images, corroborating our findings. In addition, Chen et al. the implemented algorithm enables the automatic
(2022) showed that the dimensions of nanomaterial’s quantification of the longitudinal relaxation time,
67
influence contrast, with NPs larger than 12 nm producing effectively overcoming these limitations. This tool segments
negative contrast. Our synthesized NPs, particularly Fe O different ROIs, analyzes signal intensity, and quantifies the
3
2
NPs, exhibited such a negative contrast characteristic, longitudinal relaxation time for various NPs.
wherein higher concentrations resulted in darker areas. The The reproducibility analysis of this method, validated
signal reduction effect observed with increasing Fe O NP against manual quantitative evaluations, revealed that the
2
3
concentration may be attributed to the disturbance of local algorithm effectively assists specialists in identifying subtle
magnetic field homogeneity caused by Fe O -core NPs. variations in the signal intensity. This capability is particularly
68
3
2
This perturbation causes protons to lose energy owing to valuable when using different metal oxide NPs NPs as CAs.
spin‒spin interactions in an aqueous medium, increasing For example, Fe O NPs exhibited substantial variations
2
3
the loss of coherence and consequently decreasing the in the signal intensity and relaxation time, yielding high
T2 time. 68 contrast, which aligned with the Fe magnetic properties.
As anticipated, Fe O NPs substantially impacted the Moreover, the synthesized NPs altered the relaxation time
2
3
MRI signal intensity and longitudinal relaxation time. in MRI, modifying the pixel signal intensity and displaying
67
However, the other metal oxide NPs also demonstrated negative contrast influenced by the particle size.
potential for specific applications based on their signal- This algorithmic approach is particularly valuable
altering properties in MRI. in situations wherein changes in the signal intensity
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 61 doi: 10.36922/aih.3947