Page 13 - AIH-2-3
P. 13
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in embryo selection for ART
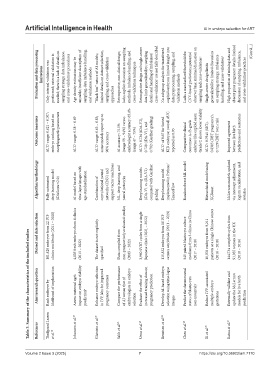
Evaluation and data processing limitations Only internal validation was performed; external validation is needed; there is a lack of details on sampling strategy, data imbalance, and cross-validation c procedures Age density estimation may be unstable; insufficient description of sampling, data imbalance handling, and validation methods “Black box” nature of AI models; limited details on dataset selection, sampling, and cross‐validation a
Outcome measures AUC a range: 0.621 – 0.707; embryo ranking based on morphogenetic parameters AUC a range: 0.58 – 0.69 AUC a range: 0.63 – 0.83; some models report up to 90% accuracy AI accuracy: 75.5% (range 59 – 94%) versus embryologist accuracy: 65.4% (range 47 – 75%) AUC a : 0.736 (iDA-V2), 0.720 (iDA-V1), and 0.702 (Gardner grading) AUC a of 0.67 for Sorted KID embryos; overall AUC reported as 0.95 Comparative clinical
Algorithm/methodology Fully automated deep learning model (iDAScore v2.0) AI model based on time‐lapse images with age-standardization Combination of convolutional neural networks (CNN) and support vector machines ML, deep learning, and neural networks Deep learning models (iDA-V1 vs. iDA-V2) compared with Gardner grading Deep learning model implemented in Python/ TensorFlow Random forest ML model Hierarchical model using
Dataset and data selection 181,428 embryos from 22 IVF clinics worldwide (2011 – 2020) 4,805 fresh embryos from 4 clinics (2013 – 2022) The dataset is not explicitly specified Data compiled from non-prospectively evaluated studies (2005 – 2022) 3,960 SVBT cycles from a single Japanese clinic (2021 – 2022) 115,832 embryos from 18 IVF centers worldwide (2011 – 2019) 345 paired blastocyst culture mediums from 3 clinics in China (2017 – 2
Table 3. Summary of the characteristics of the included studies
Aim/research question Rank embryos by likelihood of implantation Assess maternal age’s impact on embryo viability prediction b Enhance embryo selection in IVF labs for improved pregnancy outcomes Compare the performance of AI versus that of embryologists in embryo selection Evaluate the effect of increased training data on pregnancy prediction Develop AI-based embryo selection using time-lapse images Predict the chromosomal
References Theilgaard Lassen et al. 16 Johansen et al. 18 Glatstein et al. 20 Salih et al. 21 Ueno et al. 23 Berntsen et al. 24 Chen et al. 25 Xi et al. 26 Ratna et al. 27
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/aih.7170