Page 14 - AIH-2-3
P. 14
Artificial Intelligence in Health AI in embryo selection for ART
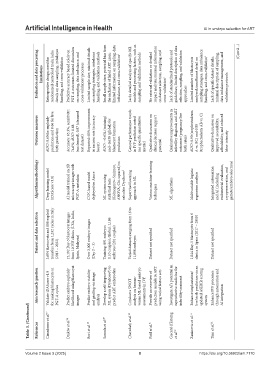
Evaluation and data processing limitations Retrospective design; need for randomized controlled trials; lacks details on data sampling, imbalance handling, and cross-validation Predictive accuracy based solely on PGT-A outcomes; limited discussion on sampling, data imbalance, and cross-validation c processes Limited sample size; minimal details on sampling strategies, imbalance handling, and validation methods Small sample sizes; potential bia
Outcome measures AUC a : 0.60 for euploidy prediction and 0.66 for live birth prediction Accuracy: 65.3%, sensitivity: 74.6%; AUC a : 0.68 (uncleaned), 0.87 (cleansed test dataset) Reported>85% improvement in success rate (accuracy boost) AUC a : ~0.634 (training) and~0.638 (global) for blastocyst formation prediction General performance trends in IVF prediction noted (no specific quantitative metric) Qualitative discussion
Algorithm/methodology Deep learning model (iDAScore v1.0) AI model trained on 2D microscope images with PGT-A metadata CNN-based model deployed on Azure ML system using statistical tests (Kolmogorov–Smirnov, ANOVA, Chi-squared) to calculate DynScore d Supervised learning approach in ML Various machine-learning techniques ML algorithms Multivariable logistic regression analysis Integrated automation and AI (including end
Dataset and data selection 3,604 blastocysts and 808 euploid transfers from 1,232 cycles in Italy (2013 – 2022) 15,192 Day-5 blastocyst images from 10 IVF clinics (USA, India, Spain, Malaysia) Over 3,000 embryo images (Day 2 – 3) Training: 891 embryos (110 couples); Global: 1,186 embryos (201 couples) Varied datasets ranging from 16 to 11,898 embryos Dataset not specified Dataset not specified 1,044 Day-5 blastocysts from 6 clinics i
Aim/research question Validate iDAScore v1.0 for ranking blastocysts in PGT-A cycles Predict embryo euploidy likelihood using blastocyst images Predict embryo viability and grading via image analysis Develop a self-improving ML system (DynScore d ) to predict ART embryo fate Conduct a SWOT analysis on human- versus ML-based embryo assessments in IVF Provide an overview of prediction models in ART using varied feature sets I
Table 3. (Continued) References Cimadomo et al. 17 Diakiw et al. 28 Bori et al. 19 Sawada et al. 29 Cheredath et al. 30 Patil et al. 31 Giscard d’Estaing et al. 32 Zaninovic et al. 14 Tian et al. 22
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/aih.7170