Page 42 - AIH-2-4
P. 42
Artificial Intelligence in Health ViT for neurodegeneration diagnosis
classification while developing the ViT solely on Considering this and the first criterion, the dataset
18 F-FDG PET scans includes the last MCI scan before progression to AD.
• Integrating a brain atlas with ViT’s attention maps This sample selection procedure resulted in a dataset of
to gain model explainability and provide more size 580. Table 1 provides the details about the dataset split
information to the user.
ratios and the number of samples.
3. Data and methods 3.2. Brain imaging technologies and techniques
3.1. Data acquisition There are several brain imaging technologies with their
Data used in the preparation of this article were obtained unique advantages and disadvantages. Thus, in this part,
from the ADNI database (adni.loni.usc.edu). The ADNI we discuss the rationale behind utilizing F-FDG PET
18
was launched in 2003 as a public-private partnership, led scans in our research.
by Michael W. Weiner, MD, as the principal investigator. A PET scan imaging session starts after injecting slight
The primary goal of ADNI has been to test whether amounts of a radioactive tracer into the subject’s veins, which
serial MRI, PET, other biological markers, and clinical spreads to the body through the blood flow. The tracer enables
and neuropsychological assessment can be combined to the PET scanning device to capture metabolic activities in
measure the progression of MCI and early AD.
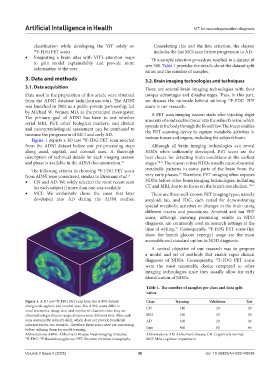
Figure 1 depicts a 3D raw F-FDG PET scan selected various tissues and organs, including the subject’s brain.
18
from the ADNI dataset before our pre-processing steps Although all brain imaging technologies can reveal
along axial, sagittal, and coronal axes. A thorough NDDs when sufficiently developed, PET scans are the
description of technical details for each imaging session best choice for detecting brain conditions at the earliest
and phase is available in the ADNI documentation. 31 stages. 10,11 The reason is that NDDs usually cause abnormal
The following criteria in choosing F-FDG PET scans metabolic patterns in some parts of the brain from the
18
10
from ADNI were considered, similar to Etminani et al.: 4 very early phases. Therefore, PET imaging often exposes
• CN and AD: We solely selected the most recent scan NDDs before other brain imaging technologies, including
for each subject if more than one was available CT and MRI, due to its focus on the brain’s metabolism. 10,11
• MCI: We exclusively chose the cases that later There are three well-known PET imaging types, namely
developed into AD during the ADNI studies. amyloid, tau, and FDG, each suited for demonstrating
special metabolic activities or changes in the brain using
different tracers and procedures. Amyloid and tau PET
scans, although showing promising results in NDD
diagnosis, are commonly used in research settings at the
time of writing. Consequently, F-FDG PET scans that
21
18
show the brain’s glucose (energy) usage are the most
accessible and standard option in NDD diagnosis.
A central objective of our research was to propose
a model and set of methods that enable rapid clinical
diagnosis of NDDs. Consequently, F-FDG PET scans
18
were the most reasonable choice compared to other
imaging technologies since they usually allow for early
identification of NDDs.
Table 1. The number of samples per class and data split
ratios
Figure 1. A 3D raw F-FDG PET scan from the ADNI dataset Class Training Validation Test
18
along axial, sagittal, and coronal axes. The ADNI scans differ in CN 140 20 20
voxel intensities, image size, and number of channels since they are
obtained using a diverse range of scanners on different sites. Also, each MCI 160 20 20
scan contains the subject’s skull, which does not provide beneficial AD 160 20 20
information for our research. Therefore, these scans need pre-processing
before utilizing them for model training. Sum 460 60 60
Abbreviations: ADNI: Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CN: Cognitively normal;
18
18 F-FDG: F-fluorodeoxyglucose; PET: Positron emission tomography. MCI: Mild cognitive impairment.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 36 doi: 10.36922/AIH025140026