Page 67 - AIH-2-4
P. 67
Artificial Intelligence in Health Synthetic data for obesity level prediction
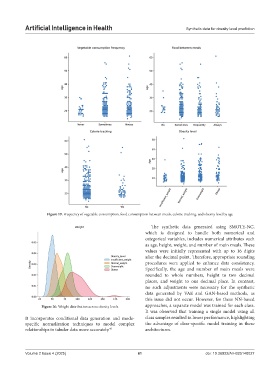
Figure 19. Frequency of vegetable consumption, food consumption between meals, calorie tracking, and obesity level by age
The synthetic data generated using SMOTE-NC,
which is designed to handle both numerical and
categorical variables, includes numerical attributes such
as age, height, weight, and number of main meals. These
values were initially represented with up to 16 digits
after the decimal point. Therefore, appropriate rounding
procedures were applied to enhance data consistency.
Specifically, the age and number of main meals were
rounded to whole numbers, height to two decimal
places, and weight to one decimal place. In contrast,
no such adjustments were necessary for the synthetic
data generated by VAE and GAN-based methods, as
this issue did not occur. However, for these NN-based
Figure 20. Weight distribution across obesity levels approaches, a separate model was trained for each class.
It was observed that training a single model using all
It incorporates conditional data generation and mode- class samples resulted in lower performance, highlighting
specific normalization techniques to model complex the advantage of class-specific model training in these
relationships in tabular data more accurately. 41 architectures.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 61 doi: 10.36922/AIH025140027