Page 104 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 104
Liu and Jusoh
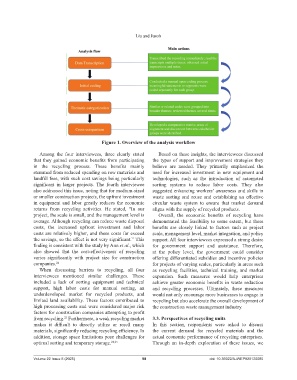
Figure 1. Overview of the analysis workflow
Among the four interviewees, three clearly stated Based on these insights, the interviewees discussed
that they gained economic benefits from participating the types of support and improvement strategies they
in the recycling process. These benefits mainly believe are needed. They primarily emphasized the
stemmed from reduced spending on raw materials and need for increased investment in new equipment and
landfill fees, with such cost savings being particularly technologies, such as the introduction of automated
significant in larger projects. The fourth interviewee sorting systems to reduce labor costs. They also
also addressed this issue, noting that for medium-sized suggested enhancing workers’ awareness and skills in
or smaller construction projects, the upfront investment waste sorting and reuse and establishing an effective
in equipment and labor greatly reduces the economic circular waste system to ensure that market demand
returns from recycling activities. He stated, “In our aligns with the supply of recycled products.
project, the scale is small, and the management level is Overall, the economic benefits of recycling have
average. Although recycling can reduce waste disposal demonstrated the feasibility to some extent, but these
costs, the increased upfront investment and labor benefits are closely linked to factors such as project
costs are relatively higher, and these costs far exceed scale, management level, market integration, and policy
the savings, so the effect is not very significant.” This support. All four interviewees expressed a strong desire
finding is consistent with the study by Ann et al., which for government support and assistance. Therefore,
also showed that the cost-effectiveness of recycling at the policy level, the government could consider
varies significantly with project size for construction offering differentiated subsidies and incentive policies
companies. 24 for projects of varying scales, particularly in areas such
When discussing barriers to recycling, all four as recycling facilities, technical training, and market
interviewees mentioned similar challenges. These expansion. Such measures would help enterprises
included a lack of sorting equipment and technical achieve greater economic benefits in waste reduction
support, high labor costs for manual sorting, an and recycling processes. Ultimately, these measures
underdeveloped market for recycled products, and would not only encourage more businesses to engage in
limited land availability. These factors contributed to recycling but also accelerate the overall development of
high processing costs and were considered major risk the construction waste management industry.
factors for construction companies attempting to profit
from recycling. Furthermore, a weak recycling market 3.3. Perspectives of recycling units
23
makes it difficult to directly utilize or resell many In this section, respondents were asked to discuss
materials, significantly reducing recycling efficiency. In the current demand for recycled materials and the
addition, storage space limitations pose challenges for actual economic performance of recycling enterprises.
optimal sorting and temporary storage. 24,25 Through an in-depth exploration of these issues, we
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 98 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025120080