Page 105 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 105
Economic analysis: Shaanxi waste recycling
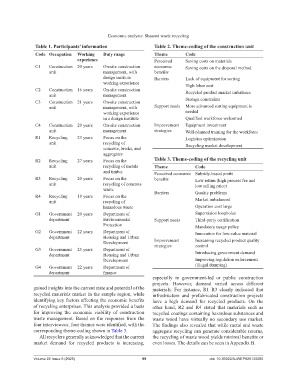
Table 1. Participants’ information Table 2. Theme‑coding of the construction unit
Code Occupation Working Duty range Theme Code
experience Perceived Saving costs on materials
C1 Construction 20 years On-site construction economic Saving costs on the disposal method
unit management, with benefits
design institute Barriers Lack of equipment for sorting
working experience High labor cost
C2 Construction 16 years On-site construction Recycled product market imbalance
unit management
C3 Construction 21 years On-site construction Storage constraints
unit management, with Support needs More advanced sorting equipment is
working experience needed
in a design institute Qualified workforce welcomed
C4 Construction 20 years On-site construction Improvement Equipment investment
unit management strategies Well-planned training for the workforce
R1 Recycling 23 years Focus on the Logistics optimization
unit recycling of Recycling market development
concrete, bricks, and
aggregates
R2 Recycling 27 years Focus on the Table 3. Theme‑coding of the recycling unit
unit recycling of metals Theme Code
and timber Perceived economic Subsidy-based profit
R3 Recycling 20 years Focus on the benefits Low return (high process fee and
unit recycling of concrete low selling price)
waste Barriers Quality problems
R4 Recycling 18 years Focus on the
unit recycling of Market imbalanced
hazardous waste Operation cost large
G1 Government 20 years Department of Supervision loopholes
department Environmental Support needs Third-party certification
Protection Mandatory usage policy
G2 Government 22 years Department of Innovation for low-value material
department Housing and Urban
Development Improvement Increasing recycled product quality
G3 Government 25 years Department of strategies control
department Housing and Urban Introducing government demand
Development Improving regulation enforcement
G4 Government 22 years Department of (illegal dumping)
department finance
especially in government-led or public construction
projects. However, demand varied across different
gained insights into the current state and potential of the materials. For instance, R1–R3 clearly indicated that
recycled materials market in the sample region, while infrastructure and prefabricated construction projects
identifying key factors affecting the economic benefits have a high demand for recycled products. On the
of recycling enterprises. This analysis provided a basis other hand, R2 and R4 stated that materials such as
for improving the economic viability of construction recycled coatings containing hazardous substances and
waste management. Based on the responses from the waste wood have virtually no secondary use market.
four interviewees, four themes were identified, with the The findings also revealed that while metal and waste
corresponding theme-coding shown in Table 3. aggregate recycling can generate considerable returns,
All recyclers generally acknowledged that the current the recycling of waste wood yields minimal benefits or
market demand for recycled products is increasing, even losses. The details can be seen in Appendix B.
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 99 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025120080