Page 109 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 109
Economic analysis: Shaanxi waste recycling
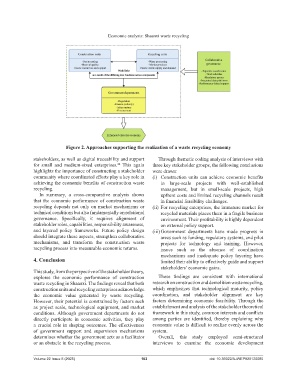
Figure 2. Approaches supporting the realization of a waste recycling economy
stakeholders, as well as digital traceability and support Through thematic coding analysis of interviews with
for small and medium-sized enterprises. This again three key stakeholder groups, the following conclusions
44
highlights the importance of constructing a stakeholder were drawn:
community where coordinated efforts play a key role in (i) Construction units can achieve economic benefits
achieving the economic benefits of construction waste in large-scale projects with well-established
recycling. management, but in small-scale projects, high
In summary, a cross-comparative analysis shows upfront costs and limited recycling channels result
that the economic performance of construction waste in financial feasibility challenges.
recycling depends not only on market mechanisms or (ii) For recycling enterprises, the immature market for
technical conditions but also fundamentally on relational recycled materials places them in a fragile business
governance. Specifically, it requires alignment of environment. Their profitability is highly dependent
stakeholder roles, capabilities, responsibility awareness, on external policy support.
and layered policy frameworks. Future policy design (iii) Government departments have made progress in
should integrate these aspects, strengthen collaborative areas such as funding, regulatory systems, and pilot
mechanisms, and transform the construction waste projects for technology and training. However,
recycling process into measurable economic returns. issues such as the absence of coordination
mechanisms and inadequate policy layering have
4. Conclusion limited their ability to effectively guide and support
stakeholders’ economic gains.
This study, from the perspective of the stakeholder theory,
explores the economic performance of construction These findings are consistent with international
waste recycling in Shaanxi. The findings reveal that both research on construction and demolition waste recycling,
construction units and recycling enterprises acknowledge which emphasizes that technological maturity, policy
the economic value generated by waste recycling. coordination, and stakeholder alignment are key
However, their potential is constrained by factors such factors determining economic feasibility. Through the
as project scale, technological equipment, and market establishment and analysis of the stakeholder theoretical
conditions. Although government departments do not framework in this study, common interests and conflicts
directly participate in economic activities, they play among parties are identified, thereby explaining why
a crucial role in shaping outcomes. The effectiveness economic value is difficult to realize evenly across the
of government support and supervision mechanisms system.
determines whether the government acts as a facilitator Overall, this study employed semi-structured
or an obstacle in the recycling process. interviews to examine the economic development
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 103 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025120080