Page 195 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 195
Use of coal gangue for mine backfill
As i increased, the slump decreased from 59.8 cm to The resulting improvement in homogeneity and
k
55.0 cm, indicating a trend of decreasing flowability pumpability ensures good construction workability.
as the particle distribution became more compact. This Therefore, i = 0.91 is considered the optimal particle
k
trend is attributed to the enhanced packing density and an grading parameter for coal gangue slurry, striking a
increased proportion of coarse particles, both of which balance between flowability and structural stability.
led to higher internal shear resistance. Meanwhile, the This grading optimization not only improves slurry
water separation and segregation rates significantly performance in engineering applications but also
decreased from 4.8% and 23.0% to 2.9% and 16.5%, promotes the high-value utilization of coal gangue and
respectively, suggesting that a higher proportion fly ash, contributing to the sustainable management of
of fine particles effectively improved the slurry’s industrial solid waste in mine backfilling.
water retention and uniformity. This improvement
mechanism can be attributed to the adsorption capacity 3.4.2. Influence of particle size matching on the curing
of fine particles (<1 mm), which reduces free water performance of the slurry
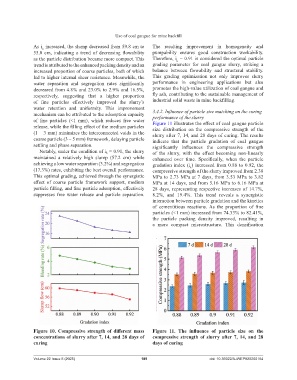
Figure 11 illustrates the effect of coal gangue particle
release, while the filling effect of the medium particles size distribution on the compressive strength of the
(1 – 3 mm) minimizes the interconnected voids in the slurry after 7, 14, and 28 days of curing. The results
coarse particle (3 – 5 mm) framework, delaying particle indicate that the particle gradation of coal gangue
settling and phase separation. significantly influences the compressive strength
Notably, under the condition of iₖ = 0.91, the slurry of the slurry, with the effect becoming non-linearly
maintained a relatively high slump (57.2 cm) while enhanced over time. Specifically, when the particle
achieving a low water separation (3.2%) and segregation gradation index (i ) increased from 0.88 to 0.92, the
k
(17.3%) rates, exhibiting the best overall performance. compressive strength of the slurry improved from 2.38
This optimal grading, achieved through the synergistic MPa to 2.73 MPa at 7 days, from 3.53 MPa to 3.82
effect of coarse particle framework support, medium MPa at 14 days, and from 5.16 MPa to 6.16 MPa at
particle filling, and fine particle adsorption, effectively 28 days, representing respective increases of 14.7%,
suppresses free water release and particle separation. 8.2%, and 19.4%. This trend reveals a synergistic
interaction between particle gradation and the kinetics
of cementitious reactions. As the proportion of fine
particles (<1 mm) increased from 74.33% to 82.41%,
the particle packing density improved, resulting in
a more compact microstructure. This densification
Figure 10. Compressive strength of different mass Figure 11. The influence of particle size on the
concentrations of slurry after 7, 14, and 28 days of compressive strength of slurry after 7, 14, and 28
curing days of curing
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 189 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025200154