Page 23 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 23
Heterogeneous catalysts for biodiesel production
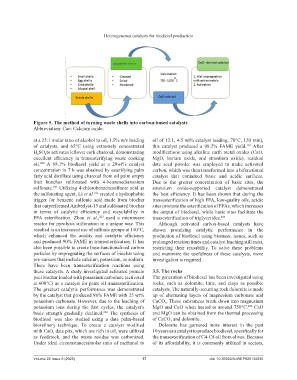
Figure 5. The method of turning waste shells into carbon-based catalysts
Abbreviation: Cao: Calcium oxide.
at a 25:1 molar ratio of alcohol to oil, 1.5% w/v loading oil of 12:1, 4.5 wt% catalyst loading, 70°C, 120 min),
of catalysts, and 65°C using extremely concentrated this catalyst produced a 98.2% FAME yield. After
101
H SO to activates leftover cork charcoal, demonstrating modifications using alkaline earth metal oxides (CaO,
4
2
excellent efficiency in transesterifying waste cooking MgO, barium oxide, and strontium oxide), residual
oil. A 98.1% biodiesel yield at a 20wt% catalyst date seed powder was employed to make activated
220
concentration in 7 h was obtained by esterifying palm carbon, which was then transformed into a bifunctional
fatty acid distillate using charcoal from oil palm empty catalyst that contained basic and acidic surfaces.
fruit bunches sulfonated with 4-benzenediazonium Due to the greater concentration of basic sites, the
sulfonate. Utilizing 4-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid as strontium oxide-supported catalyst demonstrated
221
the sulfonating agent, Li et al. created a hydrophobic the best efficiency. It has been shown that during the
222
trigger for benzene sulfonic acid made from biochar transesterification of high FFA, low-quality oils, acidic
that outperformed Amberlyst-15 and sulfonated biochar sites promote the esterification of FFAs, which increases
in terms of catalytic efficiency and recyclability in the output of biodiesel, while basic sites facilitate the
FFA esterification. Zhou et al., used a microwave transesterification of triglycerides. 225
223
reactor for pyrolysis sulfonation in a unique way. This Although activated carbon-based catalysts have
resulted in an increased use of sulfonic groups at 140°C, shown promising catalytic performance in the
which enhanced the acidity and catalytic efficiency production of biodiesel using biomass, issues, such as
and produced 90% FAME in transesterification. It has prolonged reaction times and catalyst leaching still exist,
also been possible to create base-functionalized carbon restricting their reusability. To solve these problems
particles by impregnating the surfaces of biochar using and maximize the usefulness of these catalysts, more
pre-cursors that include calcium, potassium, or sodium. investigation is required.
There have been transesterification reactions using
these catalysts. A study investigated activated pomelo 3.5. The rocks
peel biochar loaded with potassium carbonate (activated The generation of biodiesel has been investigated using
at 600°C) as a catalyst for palm oil transesterification. rocks, such as dolomite, lime, and clays as possible
The greatest catalytic performance was demonstrated catalysts. The naturally occurring rock dolomite is made
by the catalyst that produced 98% FAME with 25 wt% up of alternating layers of magnesium carbonate and
potassium carbonate. However, due to the leaching of CaCO . These substances break down into magnesium
3
potassium ions during the first cycles, the catalyst’s MgO and CaO when heated to around 750°C. CaO
226
basic strength gradually declined. The synthesis of and MgO can be obtained from the thermal processing
224
biodiesel was also studied using a date palm-based of CaCO and dolomite.
3
biorefinery technique. To create a catalyst modified Dolomite has garnered more interest in the past
with CaO, date pits, which are rich in oil, were utilized 10 years as a catalyst to produce biodiesel, specifically for
as feedstock, and the waste residue was carbonized. the transesterification of C4-C8 oil from olives. Because
Under ideal circumstances(molar ratio of methanol to of its affordability, it is commonly utilized in sectors,
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 17 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025130095