Page 11 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 11
Soybean with bacteria and humics
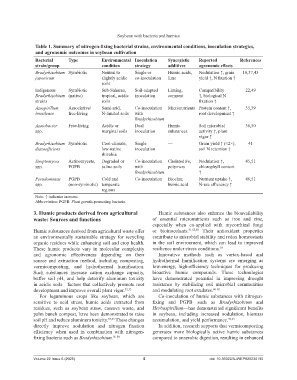
Table 1. Summary of nitrogen-fixing bacterial strains, environmental conditions, inoculation strategies,
and agronomic outcomes in soybean cultivation
Bacterial Type Environmental Inoculation Synergistic Reported References
strain/group condition strategy additives agronomic effects
Bradyrhizobium Symbiotic Neutral to Single or Humic acids, Nodulation ↑, grain 10,37,45
japonicum slightly acidic co-inoculation lime yield ↑, N fixation ↑
soils
Indigenous Symbiotic Sub-Saharan, Soil-adapted Liming, Compatibility 22,49
Bradyrhizobium (native) tropical, acidic inoculation compost ↑, biological N
strains soils fixation ↑
Azospirillum Associative/ Semi-arid, Co-inoculation Micronutrients Protein content ↑, 35,39
brasilense free-living N-limited soils with root development ↑
Bradyrhizobium
Azotobacter Free-living Acidic or Dual Humic Soil microbial 36,50
spp. marginal soils inoculation substances activity ↑, plant
vigor ↑
Bradyrhizobium Symbiotic Cool-climate, Single — Grain yield ↑ (≈2×), 41
diazoefficiens low-native inoculation soil N retention ↑
rhizobia
Streptomyces Actinomycete, Degraded or Co-inoculation Chelated Fe, Nodulation ↑, 45,51
spp. PGPB saline soils with polymers chlorophyll content
Bradyrhizobium ↑
Pseudomonas PGPB Cold and Co-inoculation Biochar, Nutrient uptake ↑, 46,51
spp. (non-symbiotic) temperate humic acid N-use efficiency ↑
regions
Note: ↑ indicates increase.
Abbreviation: PGPB: Plant growth-promoting bacteria.
3. Humic products derived from agricultural Humic substances also enhance the bioavailability
waste: Sources and functions of essential micronutrients such as iron and zinc,
especially when co-applied with mycorrhizal fungi
Humic substances derived from agricultural waste offer or bioinoculants. 31,55,58 Their antioxidant properties
an environmentally sustainable strategy for recycling contribute to microbial stability and redox homeostasis
organic residues while enhancing soil and crop health. in the soil environment, which can lead to improved
These humic products vary in molecular complexity resilience under stress conditions. 59
and agronomic effectiveness depending on their Innovative methods such as vortex-based and
source and extraction method, including composting, hydrothermal humification systems are emerging as
vermicomposting, and hydrothermal humification. low-energy, high-efficiency techniques for producing
Such substances increase cation exchange capacity, bioactive humic compounds. These technologies
buffer soil pH, and help detoxify aluminum toxicity have demonstrated potential in improving drought
in acidic soils—factors that collectively promote root resistance by stabilizing soil microbial communities
development and improve overall plant vigor. 52,53 and modulating root exudates. 60-62
For leguminous crops like soybean, which are Co-inoculation of humic substances with nitrogen-
sensitive to acid stress, humic acids extracted from fixing and PGPB—such as Bradyrhizobium and
residues, such as soybean straw, cassava waste, and Herbaspirillum—has demonstrated significant benefits
palm bunch compost, have been demonstrated to raise in soybean, including increased nodulation, biomass
soil pH and reduce aluminum toxicity. 54,55 These changes accumulation, and yield performance. 32,63
directly improve nodulation and nitrogen fixation In addition, research supports that vermicomposting
efficiency when used in combination with nitrogen- generates more biologically active humic substances
fixing bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium. 56-58 compared to anaerobic digestion, resulting in enhanced
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025230190