Page 20 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 20
Syromiatnykov
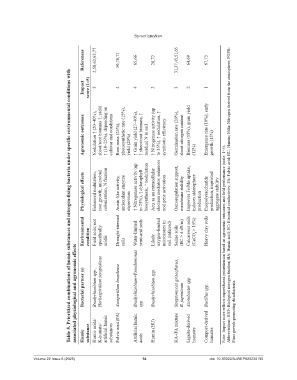
References 2,58,62,65,77 50,70,71 65,66 28,72 31,37,45,51,65 64,69 67,73
Table 5. Prioritized combinations of humic substances and nitrogen-fixing bacteria under specific environmental conditions with
Impact score (1–5) 5 4 4 3 3 2 1
Agronomic outcomes Nodulation ↑ (20–40%), shoot/root biomass ↑, yield ↑ (10–25%), depending on cultivar and conditions Root mass (25%), photosynthetic rate (15%), yield (20%) ↑ Grain yield (27–40%), ↑ shoot/root biomass, ↑ residual N in soil ↑ Nitrogenase activity (up to 35%), ↑ nodulation, ↑ symbiotic efficiency Germination rate (20%), shoot nitrogen content Biomass (18%), grain yield (12%) Emergence rate (10%), early growth (15%)
Physiological effects Enhanced nodulation, root growth, microbial colonization, N fixation Auxin-like activity, antioxidant enzyme expression ↑ Nitrogenase activity (up to 25%), ↑ chlorophyll biosynthesis, ↑ nodulation Acts as an extracellular electron mediator; enhances nod gene activation Osmoregulation support, membrane stability Improves Fe/Mn uptake, induces siderophore production Exopolysaccharide production, improved aggregate stability Ab
Environmental condition Field soils; not specifically acidic Drought-stressed soils Water-limited semi-arid soils Likely oxygen-limited microzones in soil (inferred) Saline soils (EC > 4 dS/m) Calcareous soils (CaCO 3 > 15%) Heavy clay soils Note: Impact score reflects expert-based prioritization based on agronomic outcomes and field performance (scale: 1–5).
associated physiological and agronomic effects
Bacterial partner (s) Bradyrhizobium spp., Herbaspirillum seropedicae Azospirillum brasilense Bradyrhizobium+Pseudomonas spp. Bradyrhizobium spp. Streptomyces griseoflavus, B. japonicum Azotobacter spp. Bacillus spp. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria.
Humic substance Humic acids/ K-humate/ artificial humic substances Fulvic acid (FA) Artificial humic acids Humin (HU) HA+FA mixture Lignite-derived humates Compost-derived humates
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025230190