Page 21 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 21
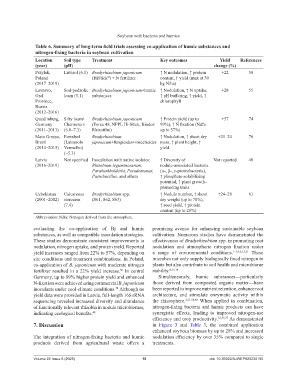
Soybean with bacteria and humics
Table 6. Summary of long-term field trials assessing co-application of humic substances and
nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soybean cultivation
Location Soil type Treatment Key outcomes Yield References
(year) (pH) change (%)
Przylek, Luvisol (6.1) Bradyrhizobium japonicum ↑ N nodulation, ↑ protein +22 50
Poland (HiStick ) + N fertilizer content, ↑ yield (max at 30
®
(2017–2019) kg N/ha)
Lavrovo, Sod-podzolic Bradyrhizobium japonicum+humic ↑ Nodulation, ↑ N uptake, +28 55
Orel loam (5.1) substances ↑ pH buffering, ↑ yield, ↑
Province, chlorophyll
Russia
(2012–2016)
Quedlinburg, Silty loam/ Bradyrhizobium japonicum ↑ Protein yield (up to +57 74
Germany Chernozem (Force 48, NPPL Hi-Stick, Biodoz 99%), ↑ N fixation (Ndfa
(2011–2013) (6.8–7.3) Rhizofilm) up to 57%)
Mato Grosso, Ferralsol Bradyrhizobium ↑ Nodulation, ↑ shoot dry +21–24 76
Brazil (Latossolo japonicum+fungicides+insecticides mass, ↑ plant height, ↑
(2014–2015) Vermelho) yield
(~5.3)
Latvia Not specified Inoculation with native isolates: ↑ Diversity of Not reported 48
(2016–2019) Rhizobium leguminosarum, nodule-associated bacteria
Paraburkholderia, Pseudomonas, (α-, β-, γ-proteobacteria),
Paenibacillus, and others ↑ phosphate-solubilizing
potential, ↑ plant growth–
promoting traits
Uzbekistan Calcareous Bradyrhizobium spp. ↑ Nodule number, ↑ shoot +24–28 61
(2001–2002) sierozem (S61, S62, S63) dry weight (up to 70%),
(7.4) ↑ seed yield, ↑ protein
content (up to 28%)
Abbreviation: Ndfa: Nitrogen derived from the atmosphere.
evaluating the co-application of Bj and humic promising avenue for enhancing sustainable soybean
substances, as well as compatible inoculation strategies. cultivation. Numerous studies have demonstrated the
These studies demonstrate consistent improvements in effectiveness of Bradyrhizobium spp. in promoting root
nodulation, nitrogen uptake, and protein yield. Reported nodulation and atmospheric nitrogen fixation under
yield increases ranged from 22% to 57%, depending on a range of environmental conditions. 1-3,5,6,12,21 These
site conditions and treatment combinations. In Poland, microbes not only supply biologically fixed nitrogen to
co-application of B. japonicum with moderate nitrogen plants but also contribute to soil health and microbiome
fertilizer resulted in a 22% yield increase. In central stability. 8,15,18
50
Germany, up to 99% higher protein yield and enhanced Simultaneously, humic substances—particularly
N-fixation were achieved using commercial B. japonicum those derived from composted organic matter—have
inoculants under cool-climate conditions. Although no been reported to improve nutrient retention, enhance root
74
yield data were provided in Latvia, full-length 16S rRNA architecture, and stimulate enzymatic activity within
sequencing revealed increased diversity and abundance the rhizosphere. 2,31,58,60 When applied in combination,
of functionally relevant rhizobia in nodule microbiomes, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and humic products can have
indicating ecological benefits. 48 synergistic effects, leading to improved nitrogen-use
efficiency and crop productivity. 32,35,77 As demonstrated
7. Discussion in Figure 3 and Table 3, the combined application
enhanced soybean biomass by up to 28% and increased
The integration of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and humic nodulation efficiency by over 35% compared to single
products derived from agricultural waste offers a treatments.
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 15 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025230190