Page 159 - {PDF Title}
P. 159
Blockchain for secure e-health data in smart cities
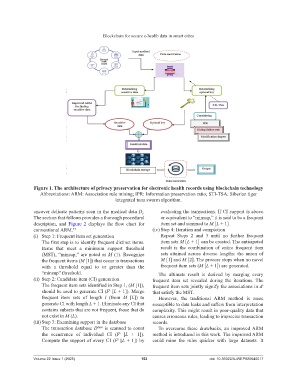
Figure 1. The architecture of privacy preservation for electronic health records using blockchain technology
Abbreviations: ARM: Association rule mining; IPR: Information preservation ratio; STI-TSA: Siberian tiger
integrated tuna swarm algorithm.
uncover delicate patterns seen in the medical data D . evaluating the transactions. If CI support is above
i
The section that follows provides a thorough procedural or equivalent to “minsup,” it is said to be a frequent
description, and Figure 2 displays the flow chart for item set and summed to M [L + 1].
conventional ARM. 37 (iv) Step 4: Iteration and completion
(i) Step 1: Frequent item set generation Repeat Steps 2 and 3 until no further frequent
The first step is to identify frequent distinct items. item sets M [L + 1] can be created. The anticipated
Items that meet a minimum support threshold result is the combination of entire frequent item
(MST), “minsup,” are noted as M (1). Recognize sets attained across diverse lengths: the union of
the frequent items (M [1]) that occur in transactions M [1] and M [2]. The process stops when no novel
with a threshold equal to or greater than the frequent item sets (M [L + 1]) are generated.
“minsup” threshold. The ultimate result is derived by merging every
(ii) Step 2: Candidate item (CI) generation frequent item set revealed during the iterations. The
The frequent item sets identified in Step 1, (M [1]), frequent item sets jointly signify the associations in d
s
should be used to generate CI (F [L + 1]). Merge that satisfy the MST.
i
frequent item sets of length l (from M [L]) to However, the traditional ARM method is more
generate CI with length L + 1. Eliminate any CI that susceptible to data leaks and suffers from interpretation
contains subsets that are not frequent, those that do complexity. This might result in poor-quality data that
not exist in M (L). causes erroneous rules, leading to imprecise transaction
(iii) Step 3: Examining support in the database records.
The transaction database D base is scanned to count To overcome these drawbacks, an improved ARM
the occurrence of individual CI (F [L + 1]). method is introduced in this work. The improved ARM
i
Compute the support of every CI (F [L + 1]) by could mine the rules quicker with large datasets. It
i
Volume 22 Issue 1 (2025) 153 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025040017