Page 80 - {PDF Title}
P. 80
Hossain, et al.
marginally improves DO levels. Biochemical oxygen approaching standard values. However, alkalinity and
demand (BOD ) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) hardness remain elevated beyond permissible limits.
5
are also elevated in untreated water, with residual levels In contrast, untreated samples, particularly Sample
in treated and PWP samples exceeding the standards of 2, exhibit the poorest water quality, characterized
0.2 mg/L and 4 mg/L, respectively. by alarmingly high bacterial loads (12,395 CFUs),
Iron levels in untreated samples (1.20 – 2.18 mg/L) elevated BOD (4.4 mg/L) and COD (5.0 mg/L), and
5
exceed the permissible limits of 1 mg/L but are excessive hardness (500 mg/L), indicating severe
substantially reduced in treated water. Arsenic contamination and extremely poor water quality. PWP
concentrations remain within permissible limits samples demonstrate intermediate water quality, but the
(0.05 mg/L) across all samples. TDS and EC values recontamination observed in Sample 2 and Sample 4
fall within acceptable limits of 1,000 mg/L and renders them less reliable for consumption compared to
700 µS/cm, respectively. pH levels are slightly treated water.
alkaline but fall within permissible ranges, while
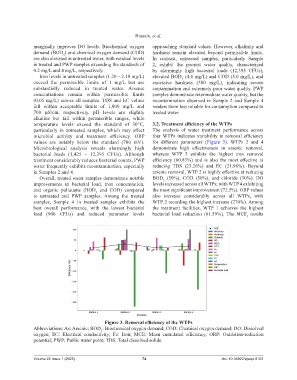
temperature levels exceed the standard of 30°C, 3.2. Treatment efficiency of the WTPs
particularly in untreated samples, which may affect The analysis of water treatment performance across
microbial activity and treatment efficiency. ORP four WTPs indicates variability in removal efficiency
values are notably below the standard (700 mV). for different parameters (Figure 3). WTPs 2 and 4
Microbiological analysis reveals alarmingly high demonstrate high effectiveness in arsenic removal,
bacterial loads (1,425 – 12,395 CFUs). Although whereas WTP 3 exhibits the highest iron removal
treatment considerably reduces bacterial counts, PWP efficiency (60.83%) and is also the most effective in
water frequently exhibits recontamination, especially reducing TDS (23.26%) and EC (21.98%). Beyond
in Samples 2 and 4. arsenic removal, WTP 2 is highly effective at reducing
Overall, treated water samples demonstrate notable BOD (50%), COD (50%), and chloride (30%). DO
5
improvements in bacterial load, iron concentration, levels increased across all WTPs, with WTP 4 exhibiting
and organic pollutants (BOD and COD) compared the most significant improvement (72.5%). ORP values
5
to untreated and PWP samples. Among the treated also increase considerably across all WTPs, with
samples, Sample 4 in treated samples exhibits the WTP 2 recording the highest increase (270%). Among
best overall performance, with the lowest bacterial the treatment facilities, WTP 1 achieves the highest
load (900 CFUs) and reduced parameter levels bacterial load reduction (61.59%). The results
Figure 3. Removal efficiency of the WTPs
Abbreviations: As: Arsenic; BOD : Biochemical oxygen demand; COD: Chemical oxygen demand; DO: Dissolved
5
oxygen; EC: Electrical conductivity; Fe: Iron; MCE: Mean cumulated efficiency; ORP: Oxidation-reduction
potential; PWP: Public water point; TDS: Total dissolved solids.
Volume 22 Issue 1 (2025) 74 doi: 10.36922/ajwep.8163