Page 72 - AJWEP-v22i3
P. 72
Saibabu, et al.
the focus of this study. The research is restricted to beyond the waste hierarchy. It is well recognized that
these districts. To achieve the objectives and test the hierarchies should be applied with flexibility, serving as
hypothesis, the data gathered are thoroughly analyzed. a broad framework for long-term ecological solutions.
As a result, this study examines a number of aspects of Despite its value, the hierarchy has been harshly and
municipal waste management procedures, incorporating frequently criticized. First, the ranking of environmental
the views of municipal corporation employees and effects may be accurate for some cases, but not for
civilian stakeholders. others.
1.5. Waste hierarchy 1.6. Objectives of the research
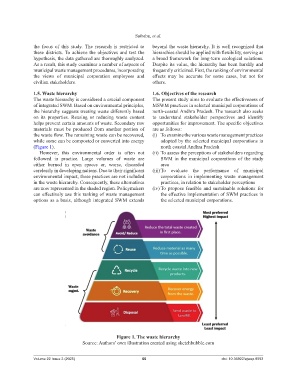
The waste hierarchy is considered a crucial component The present study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of
of integrated SWM. Based on environmental principles, MSWM practices in selected municipal corporations of
the hierarchy suggests treating waste differently based north-coastal Andhra Pradesh. The research also seeks
on its properties. Reusing or reducing waste content to understand stakeholder perspectives and identify
helps prevent certain amounts of waste. Secondary raw opportunities for improvement. The specific objectives
materials must be produced from another portion of are as follows:
the waste flow. The remaining waste can be recovered, (i) To examine the various waste management practices
while some can be composted or converted into energy adopted by the selected municipal corporations in
(Figure 1). north coastal Andhra Pradesh
However, this environmental order is often not (ii) To assess the perceptions of stakeholders regarding
followed in practice. Large volumes of waste are SWM in the municipal corporations of the study
either burned in open spaces or, worse, discarded area
carelessly in developing nations. Due to their significant (iii) To evaluate the performance of municipal
environmental impact, these practices are not included corporations in implementing waste management
in the waste hierarchy. Consequently, these alternatives practices, in relation to stakeholder perceptions
are now represented in the shaded region. Policymakers (iv) To propose feasible and sustainable solutions for
can effectively use this ranking of waste management the effective implementation of SWM practices in
options as a basis, although integrated SWM extends the selected municipal corporations.
Figure 1. The waste hierarchy
Source: Authors’ own illustration created using sketchbubble.com
Volume 22 Issue 3 (2025) 66 doi: 10.36922/ajwep.8593