Page 22 - AN-1-2
P. 22
Advanced Neurology MiR-195 regulates MS-dCA1 neural circuit in CBH rat
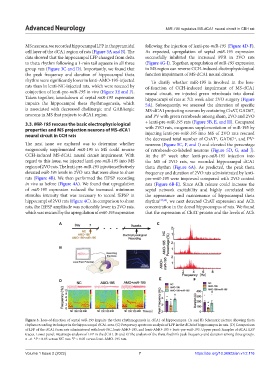
MS neurons, we recorded hippocampal LFP in the pyramidal following the injection of lenti-pre-miR-195 (Figure 4D-F).
cell layer of the dCA1 region of rats (Figure 3A and B). The As expected, upregulation of septal miR-195 expression
data showed that the hippocampal LFP changed from delta successfully inhibited the increased PPR in 2VO rats
to theta rhythm following a 1-min tail squeeze in all three (Figure 4G-I). Together, upregulation of miR-195 expression
group rats (Figure 3C and D). Importantly, we found that in MS region can reverse CCH-induced electrophysiological
the peak frequency and duration of hippocampal theta function impairment of MS-dCA1 neural circuit.
rhythm were significantly lower in lenti-AMO-195-injected To clarify whether miR-195 is involved in the loss-
rats than in lenti-NC-injected rats, which were rescued by of-function of CCH-induced impairment of MS-dCA1
coinjection of lenti-pre-miR-195 in vivo (Figure 3E and F). neural circuit, we injected green retrobeads into dorsal
Taken together, knockdown of septal miR-195 expression hippocampi of rats at 7th week after 2VO surgery (Figure
impairs the hippocampal theta rhythmogenesis, which 5A). Subsequently, we assessed the alteration of specific
is associated with decreased cholinergic and GABAergic MS-dCA1 projecting neurons by costaining ChAT, GAD67,
neurons in MS that projects to dCA1 region. and PV with green retrobeads among sham, 2VO and 2VO
3.3. MiR-195 rescues the basic electrophysiological + lenti-pre-miR-195 rats (Figure 5B, E, and H). Compared
properties and MS projection neurons of MS-dCA1 with 2VO rats, exogenous supplementation of miR-195 by
neural circuit in CCH rats injecting lenti-pre-miR-195 into MS of 2VO rats rescued
the decreased total number of ChAT , GAD67 , and PV
+
+
+
The next issue we explored was to determine whether neurons (Figure 5C, F, and I) and elevated the percentage
exogenously supplemented miR-195 in MS could reverse of retrobeads-co-labeled neurons (Figure 5D, G, and J).
CCH-induced MS-dCA1 neural circuit impairment. With At the 8 week after lenti-pre-miR-195 injection into
th
regard to this issue, we injected lenti-pre-miR-195 into MS the MS of 2VO rats, we recorded hippocampal dCA1
region of 2VO rats. The lenti-pre-miR-195 injection effectively theta rhythm (Figure 6A). As predicted, the peak theta
elevated miR-195 levels in 2VO rats that were close to sham frequency and duration of 2VO rats administrated by lenti-
rats (Figure 4B). We then performed the fEPSP recording pre-miR-195 were improved compared with 2VO control
in vivo as before (Figure 4A). We found that upregulation rats (Figure 6B-E). Since ACh release could increase the
of miR-195 expression reduced the increased minimum septal network excitability and highly correlated with
stimulus intensity that was necessary to record fEPSP in the appearance and maintenance of hippocampal theta
hippocampi of 2VO rats (Figure 4C). In comparison to sham rhythm [37,38] , we next detected ChAT expression and ACh
rats, the fEPSP amplitude was noticeably lower in 2VO rats, concentration in the dorsal hippocampus of rats. We found
which was rescued by the upregulation of miR-195 expression that the expression of ChAT protein and the levels of ACh
A C
B
D E F
Figure 3. Loss-of-function of septal miR-195 impairs the theta rhythmogenesis in dCA1 of hippocampus. (A and B) Schematic picture showing theta
rhythm recording technique in the hippocampal dCA1 area. (C) Frequency spectrum analysis of LFP in the dCA1of hippocampus in rats. (D) Comparison
of LFP of the dCA1 from rats administered with lenti-NC, lenti-AMO-195, and lenti-AMO-195 + lenti-pre-miR-195. Upper panel: Samples of dCA1 LFP
traces. Lower panel: Heatmaps analysis of LFP in the dCA1. (E and F) The analysis of the theta rhythm’s peak frequency and duration among three groups.
n =6. *P < 0.05 versus NC rats. P < 0.05 versus lenti-AMO-195 rats.
#
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i2.116