Page 25 - AN-1-2
P. 25
Advanced Neurology MiR-195 regulates MS-dCA1 neural circuit in CBH rat
A C
B
D E F G
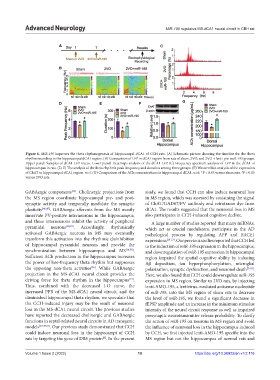
Figure 6. MiR-195 improves the theta rhythmogenesis of hippocampal dCA1 of CCH rats. (A) Schematic picture showing the timeline for the theta
rhythm recording in the hippocampal dCA1 region. (B) Comparison of LFP in dCA1 region from rats of sham, 2VO, and 2VO + lenti-pre-miR-195 groups.
Upper panel: Samples of dCA1 LFP traces. Lower panel: Heatmaps analysis of the dCA1 LFP. (C) Frequency spectrum analysis of LFP in the dCA1 of
hippocampus in rats. (D, E) The analysis of the theta rhythm’s peak frequency and duration among three groups. (F) Western blot analysis of the expression
of ChAT in hippocampal dCA1 region. n=4. (G) Comparison of the ACh concentrations in hippocampal dCA1. n=6. *P < 0.05 versus sham rats. P < 0.05
#
versus 2VO rats.
GABAergic components . Cholinergic projections from study, we found that CCH can also induce neuronal loss
[35]
the MS region coordinate hippocampal pre- and post- in MS region, which was assessed by costaining the signal
synaptic activity and temporally modulate the synaptic of ChAT/GAD67/PV antibody and retrotracer dye from
plasticity [46,47] . GABAergic afferents from the MS mostly dCA1. The results suggested that the neuronal loss in MS
innervate PV-positive interneurons in the hippocampus, also participates in CCH-induced cognitive decline.
and these interneurons inhibit the activity of peripheral A large number of studies reported that many miRNAs,
pyramidal neurons [48,49] . Accordingly, rhythmically which act as crucial modulators, participate in the AD
activated GABAergic neurons in MS may eventually pathological process by regulating APP and BACE1
transform this activation into the rhythmic disinhibition expressions [20-23] . Our previous studies reported that CCH led
of hippocampal pyramidal neurons and provide the to the reduction of miR-195 expression in the hippocampus,
synchronization between hippocampus and MS [14,50] . and downregulation of miR-195 expression in hippocampal
Sufficient ACh production in the hippocampus increases region impaired the spatial cognitive ability by inducing
the power of low-frequency theta rhythm but suppresses Aβ deposition, tau hyperphosphorylation, microglial
the opposing non-theta activities . While GABAergic polarization, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal death [7-10] .
[36]
projection in the MS-dCA1 neural circuit provides the Here, we also found that CCH could downregulate miR-195
driving force for theta rhythm in the hippocampus . expression in MS region. Similar to 2VO rats, by injecting
[14]
Thus, combined with the decreased I-O curve, the lenti-AMO-195, a lentivirus-mediated antisense nucleotide
increased PPR of the MS-dCA1 neural circuit, and the of miR-195, into the MS region of sham rats to decrease
diminished hippocampal theta rhythm, we speculate that the level of miR-195, we found a significant decrease in
the CCH-induced injury may be the result of neuronal fEPSP amplitude and an increase in the minimum stimulus
loss in the MS-dCA1 neural circuit. The previous studies intensity of the neural circuit response as well as impaired
have reported the decreased cholinergic and GABAergic presynaptic neurotransmitter release probability. To clarify
functions in septal-related neural circuits in AD transgenic the action of miR-195 on neurons in MS region and avoid
models [17,47,51] . Our previous study demonstrated that CCH the influence of neuronal loss in the hippocampus induced
could induce neuronal loss in the hippocampi of CCH by CCH, we first injected lenti-AMO-195 specific into the
rats by targeting the gene of DR6 protein . In the present MS region but not the hippocampus of normal rats and
[8]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i2.116